NCERT Solutions-Class 8: Science: Microorganism: Friend and Foe
NCERT notes alongwith solutions for class 8 science “Microorganism: Friend and Foe” are provided here. The notes as well as solutions are very much helpful for the students to understand the topics. The solutions will be handy for quickly completing the homework and preparing for exams.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction: Microorganism
- The term “Microorganism” is derived from two words: micro,” meaning very small, and “organism,” referring to a living being . Thus, a microorganism is a tiny organism that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- To observe microorganisms, we require devices like magnifying glasses or microscopes.
- These tiny organism are also known as microbes.
- Microorganisms may be single-celled like bacteria, some algae and protozoa, or multicellular, such as many algae and fungi.
Classification of Microorganism
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Protozoa
- Algae
Apart from these, there are viruses, which are also microscopic but differ from other microorganisms. Viruses can reproduce only inside the cells of a host organism, which may be a bacterium, plant, or animal.
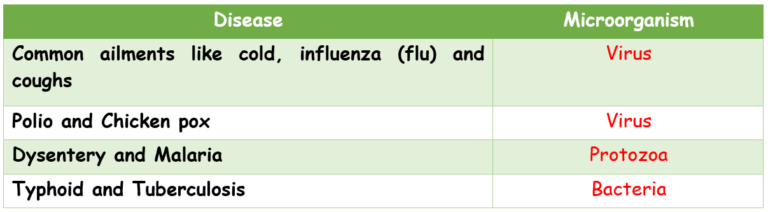
The table below lists various diseases and the microorganisms responsible for them.
Where do Microorganism live?
Microorganisms thrive in all types of environments, including extreme conditions where most other life forms cannot survive. They can be found in:
- Natural environments such as soil, water, and air.
- Extreme environments like hot springs, volcanoes, deep-sea hydrothermal vents, Antarctic ice and glaciers, highly saline areas, and acidic or alkaline conditions.
- Inside living organisms, including humans, animals, and plants.
- Man-made environments, such as fermented foods, sewage, and wastewater treatment plants.
Microorganism and Us
- Some microorganisms are beneficial in many ways whereas some others are harmful and cause diseases to us.
- On this basis, we can say there are two types of microbes: Good Microbes (Friendly Microbes) and Bad Microbes.
Good Microbes
- Making of Curd and Bread
- Curd is made by fermenting milk using a bacteria called Lactobacillus which improves gut health and digestion.
- Bacteria and Yeast are helpful for fermentation of rice idlis and dosa batter.
- Commercial use of microbes
- Fermentation is the process of converting sugars into alcohol with the help of microorganisms.
- Louis Pasteur discovered the process of fermentation in 1857.
- Yeast is used in the commercial production of alcohol and wine through fermentation.
- To produce alcohol, yeast is grown on natural sugars found in grains such as barley, wheat, and rice, where it converts these sugars into alcohol.
- Medicinal Use of Microorganism
- An antibiotic is a substance produced by microorganisms (such as bacteria and fungi) that can kill or inhibit the growth of other harmful microorganisms, especially bacteria.
- Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections in humans, animals and Plants.
- Alexander Fleming discovered Penicillin, an antibiotic, which is produced by fungus.
- Streptomycin, tetracycline and erythromycin are some of the commonly known antibiotics which are made from fungi and bacteria.
- Vaccine
- Vaccines work on the principle that when dead or weakened microbes (antigens) are introduced into a healthy body, the immune system responds by producing antibodies to fight and eliminate the invaders. These antibodies remain in the body, providing long-term protection against the disease-causing microbes.
- Vaccines help the body build immunity against diseases without the risks associated with a full-blown infection.
- Edward Jenner discovered the smallpox vaccine in 1798.
- For example – Mycobacterium bovis is used to produce the BCG vaccine.
- Increasing Soil Fertility
- Microorganisms play a vital role in improving soil fertility by enhancing nutrient availability, decomposing organic matter, and forming beneficial relationships with plants.
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria such as Rhizobium, Azotobacter, and Cyanobacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) into ammonia (NH₃), a form that plants can absorb. This process increases nitrogen availability in the soil, thereby improving its fertility.
- Cleaning the Environment
- Microorganisms decompose dead organic matter from plants and animals, breaking it down into simpler substances. These substances are then reused by other plants and animals, maintaining the natural cycle.
- Microbes also help degrade harmful and foul-smelling waste, contributing to environmental cleanliness.
Harmful Effects of Microorganism
- Disease – causing Microorganisms in Humans
- Pathogens enter our body through the air we breathe, the water we drink or the food we eat.
- They can also get transmitted by direct contact with an infected person or carried by an animal.
- Communicable diseases are microbial infections that spread from an infected person to a healthy individual through air, water, food, or physical contact. Examples include cholera, the common cold, chickenpox, and tuberculosis.
- Certain insects and animals act as carriers of disease-causing microbes. For example:
- Flies pick up pathogens from garbage and animal waste. When they land on uncovered food, they transfer these pathogens, potentially causing illness in those who consume the contaminated food.
- Mosquitoes are major carriers of diseases:
- The female Anopheles mosquito carries Plasmodium, the parasite responsible for malaria.
- The female Aedes mosquito transmits the dengue virus.
How can we control the spread of malaria or dengue?
Disease causing Microorganisms in Animals
- Anthrax is a dangerous human and cattle disease caused by a bacterium.
- Robert Koch discovered the bacterium (Bacillus Anthracis) which causes anthrax disease.
- Foot and mouth disease of cattle is caused by a virus.
Disease causing Microorganisms in Plants
- Citrus Canker is caused by bacteria.
- Rust of wheat is caused by fungi.
- Yellow vein or Mosaic of bhindi (Okra) is caused by virus.
Food Poisoning
Food Preservation
Food poisoning is an illness that results from consuming contaminated food or beverages. It occurs due to the presence of harmful microorganisms, toxins, or chemicals in food. The most common causes include bacteria, viruses, parasites, and toxins.
Let`s discuss some of the common methods of preserving food at homes.
- Chemical Method
- Certain chemicals, such as salts and edible oils, are commonly used to prevent the growth of microorganisms. These substances are known as preservatives. Some commonly used preservatives include sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite.
- Preservation by Common Salt – Common salt is used to preserve foods like meat, fish, amla, raw mangoes, and tamarind by preventing microbial growth.
- Preservation by Sugar – Jams, jellies, and squashes are preserved using sugar, as it reduces moisture content, inhibiting bacterial growth.
- Preservation by Oil and Vinegar – Pickles are preserved using oil and vinegar, as bacteria cannot survive in such an environment.
- Heat and Cold Treatments
- Pasteurization – Pasteurization is a heat treatment process used to kill harmful microorganisms in food and beverages while preserving their quality and nutritional value.
- In the pasteurization of milk, it is heated to around 70°C for 15 to 30 seconds, then rapidly cooled and stored. This process prevents microbial growth.
- Pasteurization was discovered by Louis Pasteur.
- Refrigeration – Storing food at low temperatures inhibits the growth of microorganisms, preventing spoilage.
- Storage and Packaging – Sealed, airtight packaging protects food from microbial contamination and extends its shelf life.
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) into nitrogenous compounds (such as ammonia, nitrates or nitrites) that plants can utilize.
Rhizobium plays a crucial role in nitrogen fixation in leguminous plants such as pulses. It resides in the root nodules of plants like beans and peas, forming a symbiotic relationship, where the bacteria provide nitrogen to the plant, and in return, the plant provides nutrients to the bacteria.
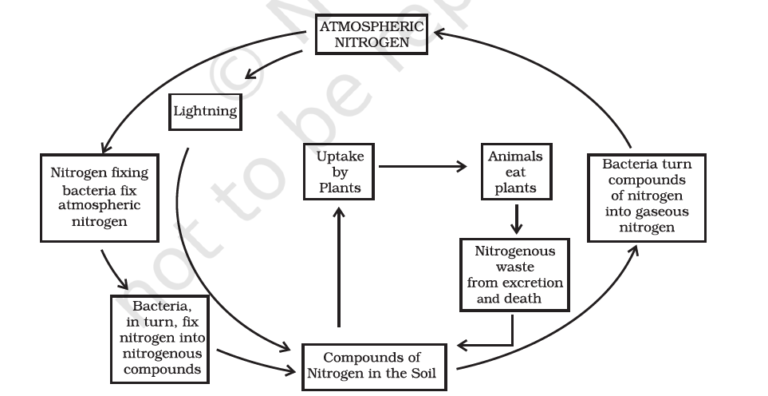
Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen Cycle takes place in the following steps:
- Plants and animals cannot directly absorb atmospheric nitrogen. Instead, certain bacteria (Rhizobium, Azotobacter) and blue-green algae (Anabaena) present in the soil convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous compounds through nitrogen fixation.
- Once nitrogen is converted into these usable compounds, plants absorb them through their roots and utilize them for the synthesis of proteins and other essential compounds.
- Animals obtain nitrogen by consuming plants, thereby incorporating nitrogenous compounds into their bodies.
- When plants and animals die, bacteria and fungi decompose their remains, converting nitrogenous wastes back into nitrogenous compounds, which plants can reuse. Some bacteria also convert a portion of these compounds back into nitrogen gas, releasing it into the atmosphere. This cycle ensures that the percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere remains stable.
Exercise
Fill in the blanks
(a) Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a ____________.
(b) Blue green algae fix __________ directly from air and enhance fertility
of soil.
(c) Alcohol is produced with the help of __________.
(d) Cholera is caused by __________.
Sol:
(a) Microscope
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Yeast
(d) Bacteria
Tick (choose) the correct answer.
(a) Yeast is used in the production of
(i) sugar (ii) alcohol (iii) hydrochloric acid (iv) oxygen
(b) The following is an antibiotic
(i) Sodium bicarbonate (ii) Streptomycin (iii) Alcohol (iv) Yeast
(c) Carrier of malaria-causing protozoan is
(i) female Anopheles mosquito (ii) cockroach (iii) housefly (iv) butterfly
(d) The most common carrier of communicable diseases is
(i) ant (ii) housefly (iii) dragonfly (iv) spider
(e) The bread or idli dough rises because of
(i) heat (ii) grinding (iii) growth of yeast cells (iv) kneading
(f) The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called
(i) nitrogen fixation (ii) moulding (iii) fermentation (iv) infection
Sol:
(a) Alcohol
(b) Streptomycin
(c) female Anopheles mosquito
(d) housefly
(e) growth of yeast cells
(f) fermentation
Match the organisms in Column A with their action in Column B.
| 1. Bacteria | (i) Fixing nitrogen |
|---|---|
| 2. Rhizobium | (ii) Setting of curd |
| 3. Lactobacillus | (iii) Baking of bread |
| 4. Yeast | (iv) Causing malaria |
| 5. A Protozoan | (v) Causing cholera |
| 6. A Virus | (vi) Causing AIDS |
| 1. Bacteria | (v) Causing cholera |
|---|---|
| 2. Rhizobium | (i) Fixing nitrogen |
| 3. Lactobacillus | (ii) Setting of curd |
| 4. Yeast | (iii) making of bread |
| 5. A Protozoan | (iv) Causing malaria |
| 6. A Virus | (vi) Causing AIDS |
Can microorganisms be seen with the naked eye? If not, how can they be seen?
Sol:
No. Microorganism cannot be seen with the naked eye. We need devices like magnifying glass or microscope to see microorganism with our naked eye.
What are the major groups of microorganisms?
Microorganisms are classified into four major groups. These are:
1. Bacteria
2. Fungi
3. Protozoa
4. Algae
What are the major groups of microorganisms?
Rhizobium, Azotobacter etc. are the microorganism that can fix the atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Write 10 lines on the usefulness of microorganisms in our lives.
Microorganisms play a crucial role in various applications as discussed below:
i. Lactobacillus is used in the preparation of curd.
ii. Bacteria helps in the making of cheese, pickles and many other food items.
iii. Bacteria and yeast aid in fermentation of rice idlis and dosa batter.
iv. Yeast is used in the baking industry for making breads, cakes and pastries.
v. Yeast is also used for commercial production of alcohol and wine.
vi. Microorganism are used for large scale production of acetic acid i.e. vinegar.
vii. Certain microorganism, such as Bacteria and Fungi, are used for the production of antibiotics like Streptomycin, tetracycline and erythromycin.
viii.Dead or weakened microbes are used in the preparation of vaccines.
ix.Certain Bacteria, such as Rhizobium and Azotobacter, fix atmospheric nitrogen and enhance soil fertility.
x.Microorganisms act as natural cleansing agents by decompose waste into manure, promoting environmental sustainability.
Write a short paragraph on the harmful effects of microorganisms.
Microorganisms are harmful in many ways, causing diseases in humans, animals, and plants. In humans, bacterial infections include tuberculosis, cholera, and typhoid, while viral diseases include measles, chickenpox, and polio. Protozoa cause illnesses such as malaria and dengue. Similarly, microorganisms affect animals, with bacteria causing anthrax and viruses leading to foot and mouth disease. Plants like wheat, rice, potato, sugarcane, orange, and apple are also vulnerable to microbial infections. For instance, citrus canker is caused by bacteria, rust of wheat by fungi, and yellow vein mosaic of bhindi (okra) by a virus.
What are antibiotics? What precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics?
Antibiotics are substances produced by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, that can kill or inhibit the growth of other harmful bacteria. However, their use should be carefully regulated. It is essential to take antibiotics only under the guidance of a qualified doctor and to complete the prescribed course. Misuse, such as taking antibiotics when not needed or in incorrect doses, can reduce their effectiveness in the future. Additionally, unnecessary antibiotic use may destroy beneficial bacteria in the body, potentially leading to health complications.