NCERT Solutions-Class 8: Science: Crop Production and Management
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
All living organisms require food to get energy. This energy is utilised by the organisms for proper growth, functioning and maintenance of good health of their body.
Plants can make their food by themselves. Animals including humans cannot make their own food. So, they get their food either from plants or by other animals.

Crop
- When plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. For example- a crop of wheat means that all the plants grown in a field are that of wheat.
- Crops are of different types like cereals, vegetables and fruits. These can be classified on the basis of the season in which they grow.
Types of Crops
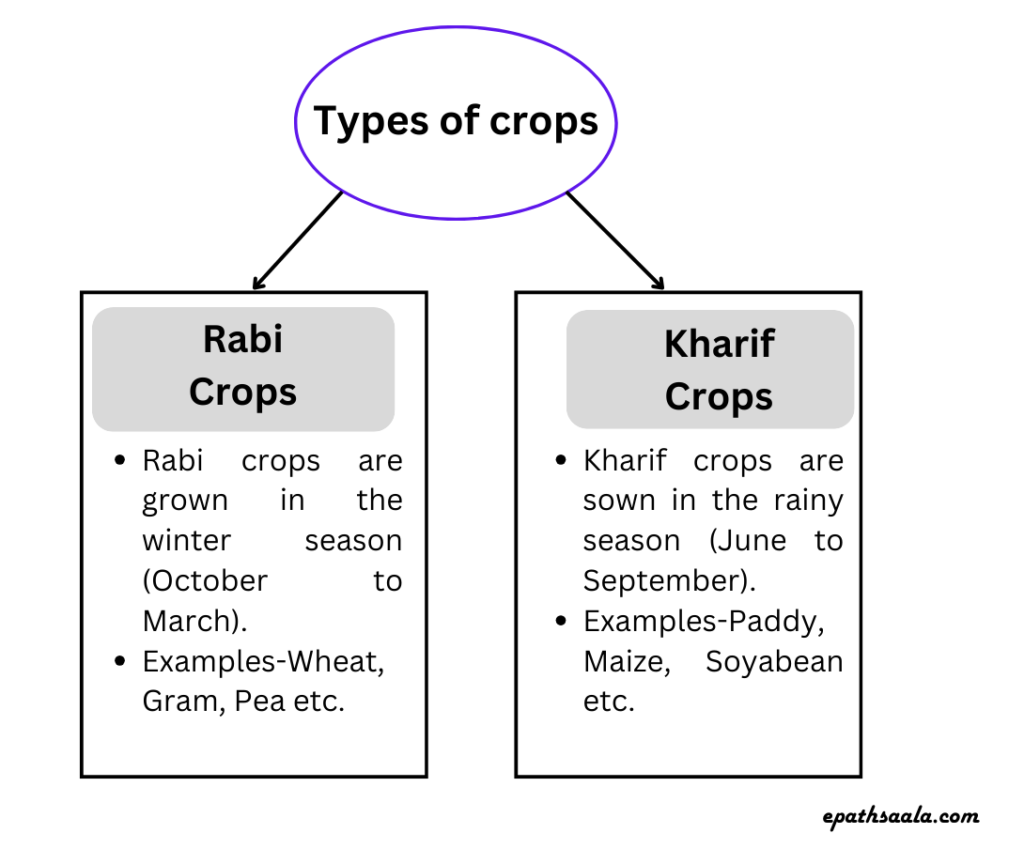
- In India two major types of crops are grown:
- Rabi Crops
- Kharif Crops
Agricultural Practices
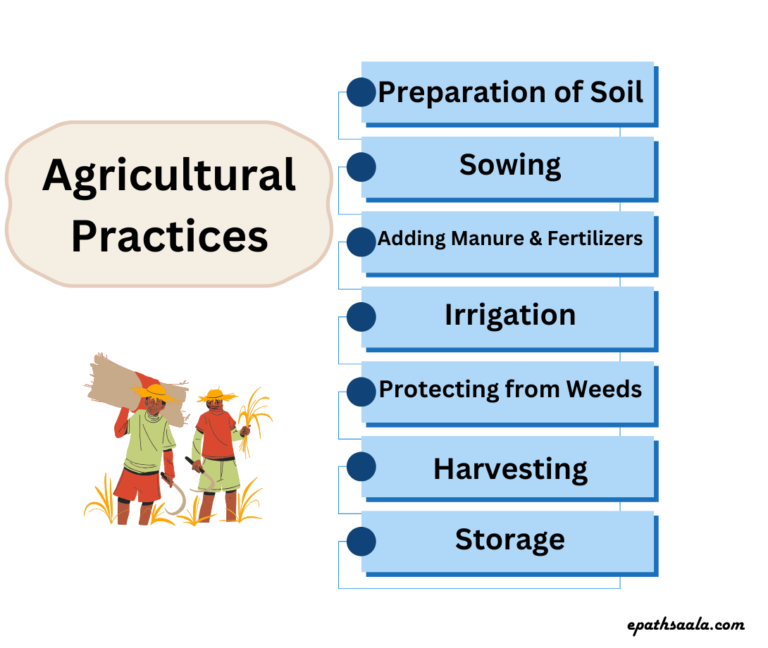
- Cultivation of crops involves several activities undertaken by the farmers over a period of time. These activities are referred to as agricultural practices which are listed below:
- Preparation of soil
- Sowing
- Adding manure and fertilizers
- Irrigation
- Protecting from weeds
- Harvesting
- Storage
Preparation of Soil
- Under this, the farmers break the soil, loosen it and turn it. The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing.
- Turning and loosening the soil brings nutrient rich soil to the top so that plants can use these nutrients.
- This also allows better root penetration, improve aeration, and integrate organic matter into the soil.
Agricultural Implements used in the preparation of soil
- Important agricultural tools used in the preparation of soil are:–
- Plough
- Hoe
- Cultivators
Plough
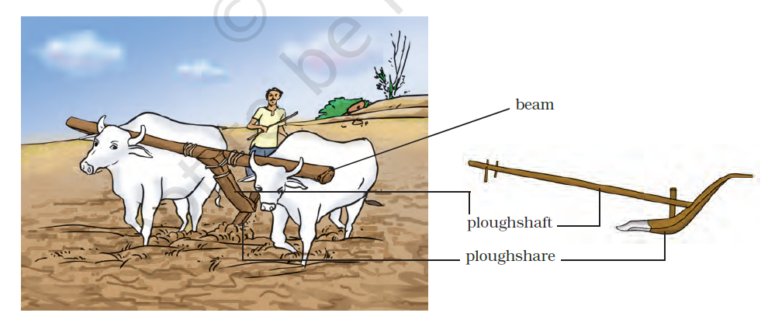
- Plough is an agricultural tool that is used for breaking, loosening and turning the soil.
- The traditional plough is generally made of wood and is drawn by a pair of bulls or other animals (horses and camels).
- The key parts of a wooden plough are- Beam, Ploughshare, Ploughshaft and Handle.
- Beam is a long horizontal wooden shaft that is placed at the bull`s neck. The beam connects the plough to the animal.
- Ploughshare: A sharp, flat blade that cuts the soil. The ploughshare was often made from iron and attached to the wooden frame.
- Ploughshaft: It is a long log of wood. One end of the ploughshaft is connected with the handle while the other end is connected with the beam.
- Handle: It is used for guiding and steering the plough.
Hoe
- It is a simple tool which is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil.
- It has a long rod of wood or iron.
- A strong, broad and bent plate of iron is fixed to one of its ends and works like a blade.

Cultivators
- Cultivators are basically the type of tillage implements used to break up the soil and removes weeds in rows.
- Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor-driven cultivator.
- The use of cultivator saves labour and time.

Sowing
- Sowing is the process of planting seeds into the soil to grow crops.
- It involves placing seeds in soil and nurturing them with water, light, and nutrients to allow them to sprout and grow into mature plants.
- A good quality, clean and healthy seeds of a good variety should be taken for sowing.

Methods of Sowing
- There are several methods farmers use to sow their seeds. Each method has its own advantages and is suited to specific types of crops. These methods are:
- Traditional
- Broadcasting
- Dibbling
- Drilling
- Seed Dropping behind the Plough
- Transplanting
- Hill Dropping
- Check Row Planting
Traditional
- A funnel-shaped tool is used to sow the seeds.
- The funnel is filled with seeds and the seeds pass through two or three sharp ended pipes that penetrate the soil.
- These ends enter into the soil and deposits the seeds at the appropriate depth.
Broadcasting
- Broadcasting involves spreading the seeds evenly over the seedbed either by hand or by using a mechanical device and then covered it with soil.
- This method is generally used for crops like wheat, rice, legumes etc. The broadcasting method is often used when a large number of seeds need to be sown.
Dibbling
- In the dibbling method, holes are made in the seedbeds at specific depths. Seeds are then placed in these holes and covered with soil. This method is mostly used for sowing vegetable crops.
Drilling
- Seeds are put into furrow lines in a continuous flow and covered with soil. This can be done either mechanically or manually. The appropriate number of seeds are sown at the proper depth and spacing.
Seed Dropping Behind the Plough
- This method is often used in villages to sow maize, peas, wheat, barley, and gram. In this process, the seeds are dropped in furrows behind the plough by a device called Malobansa. However, this procedure requires a significant amount of time and effort.
Transplanting
- In this process, seedlings are first planted in nurseries before being transplanted into prepared fields. It is generally used to cultivate vegetables and flowers. A transplanter is used for this purpose.
Hill Dropping
- In this type of sowing, the selected seeds are dropped at regular spaces but not in a continuous manner.
Check Row Planting
- The seeds are placed in straight, parallel furrows. This method involves using a check row planter. Row-to-row and plant-to-plant distances are uniform.

Tools used in Sowing
- Traditional Tools and Seed Drill are the two tools that are used in sowing.
Traditional Tools
- It is a funnel shaped like tool that is used for sowing seeds.
- The seeds are filled into the funnel, passed down through two or three pipes having sharp ends.
- These ends pierce into the soil and place seeds there.
Seed Drill
- Seed drill is an agricultural equipment used for placing the seeds uniformly at equal distance with depth with an arrangement of covering the seeds with soil.
- This protects seeds from being eaten by birds. Sowing by using a seed drill saves time and labour.
Adding Manure and Fertilizers
- The substances which are added to the soil in the form of nutrients for the healthy growth of plants is called manure and fertilisers.
Manure
- Manure is an organic substance obtained from the decomposition of plant or animal wastes.
- The use of manure improves soil texture as well as its water retaining capacity.
- It replenishes the soil with nutrients.
Fertilizer
- Fertilisers are chemicals which are rich in a particular nutrient.
- Fertilisers are produced in factories.
- Some examples of fertilisers are— urea, ammonium sulphate, super phosphate, potash, NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium).
- The use of fertilisers has helped farmers to get better yield of crops such as wheat, paddy and maize.
Why adding manure/fertilizer is required in the soil?
- Soil supplies mineral nutrients to the crop plants which are essential for the proper growth of crops. Due to continuous cultivation of crop, nutrients present in the soil start diminishing. Consequently, the crops become weak. So, to replenish the nutrients the farmers add manure in the soil for proper growth of the crops.
Substitute of Fertilizers
- Excessive use of fertilizers has made the soil less fertile.
- Fertilisers have also become a source of water pollution. Therefore, in order to maintain the fertility of the soil, we have to substitute the fertilisers.
- The substitute of fertilizers is:
- Use of organic manure
- Leave the field uncultivated (fallow) in between two crops.
- Crop rotation. This is done by growing different crops alternately. Farmers in northern India used to grow legumes as fodder in one season and wheat in the next season. This helped in the replenishment of the soil with nitrogen.
Differences between Fertilizers and Manure
| Sl. No. | Fertilizer | Manure |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fertilizers is a man-made inorganic salt. | Manue is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung and plant residues. |
| 2. | Fertilzers is prepared in factories. | Manure can be prepared in the fields. |
| 3. | Fertilizers does not provide any humus to the soil. | Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil. |
| 4. | Fertilizers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. | Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients. |
Why Organic Manure is considered better than the Fertilizers
- The organic manure is considered better than fertilisers. This is because:
- it enhances the water holding capacity of the soil.
- it makes the soil porous due to which exchange of gases becomes easy.
- it increases the number of friendly microbes.
- it improves the texture of the soil.
Irrigation
- The supply of water to crops at regular intervals is called irrigation.
Why Irrigation is essential for the plants?
- Plants contain nearly 90% water. The roots of the plant absorbed water alongwith minerals and fertilizers. Nutrients dissolved in water are transported to each part of the plant. Plants use these minerals for their proper growth and development. Water also protects the plant from deep frost and hot air currents.Thus, irrigation is essential for the plants.
Sources of Irrigation
- The sources of water for irrigation are— wells, tubewells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams and canals.
Traditional Methods of Irrigation
- The water available in wells, lakes and canals is lifted up by different methods in different regions, for taking it to the fields. The various traditional ways are:
- moat (pulley-system)
- chain pump
- dhekli, and
- rahat (Lever system)
Modern Methods of Lifting Water
- Modern methods of irrigation help us to use water economically. The main methods used are as follows:
- Sprinkler System: This system is more useful on the uneven land where sufficient water is not available. The perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top, are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. The water comes out from the rotating nozzles. It gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining. Sprinkler is very useful for lawns, coffee plantation and several other crops.
- Drip system: This system is used in those regions where availability of water is very poor. In this system, the water falls drop by drop directly near the roots. It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees.
Protection from Weeds
- In a field many other undesirable plants may grow naturally along with the crop. These undesirable plants are called weeds. The removal of weeds is called weeding.
Why weeding is necessary?
- Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light. Thus, they affect the growth of the crop.
- Some weeds interfere even in harvesting and may be poisonous for animals and human beings. Therefore, it is necessary to remove weeds from the field.
Methods of removing weeds
- Farmers adopt many ways to remove weeds and control their growth. These methods are:
- Tilling: Tilling before sowing of crops helps in uprooting and killing of weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed with the soil. The best time for the removal of weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds.
- Manual Removal: The manual removal includes physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground, from time to time. This is done with the help of a khurpi. A seed drill is also used to uproot weeds.
- Use of Weedicides: Weeds are also controlled by using certain chemicals, called weedicides like 2,4-D. These are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds. They do not damage the crops. The weedicides are diluted with water to the extent required and sprayed in the fields with a sprayer.
Harvesting
- The cutting of crop after it is mature is called harvesting.
- In harvesting, crops are pulled out or cut close to the ground.
- Harvesting in our country is either done manually by sickle or by a machine called harvester.
- In the harvested crop, the grain seeds need to be separated from the chaff. This process is called threshing. This is carried out with the help of a machine called ‘combine’ which is in fact a harvester as well as a thresher.
- Farmers with small holdings of land do the separation of grain and chaff by winnowing.
- Special festivals associated with the harvest season are Pongal, Baisakhi, Holi, Diwali, Nabanya and Bihu.
Storage
- Storage of produce is an important task.
- If the harvested grains are to be kept for longer time, they should be safe from moisture, insects, rats and microorganisms.
- Farmers store grains in jute bags or metallic bins. However, large scale storage of grains is done in silos and granaries to protect them from pests like rats and insects.
Why the harvested crops are dried before storage?
- Harvested grains contain more moisture.
- If freshly harvested grains (seeds) are stored without drying, they may get spoilt or attacked by organisms, making them unfit for use or for germination.
- Hence, before storing them, the grains are properly dried in the sun to reduce the moisture in them. This prevents the attack by insect pests, bacteria and fungi.
Food and animals
- Like plants, animals also provide us with different kinds of food.
- Animals reared at home or in farms, have to be provided with proper food, shelter and care.
- When this is done on a large scale, it is called animal husbandry.
Exercise
1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____________.
(b) The first step before growing crops is _____________ of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would _____________ on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and _____________ and _____________ from the soil are essential.
Sol:
(a) crop
(b) preparation of the soil
(c) float
(d) water and nutrients
2. Match items in column A with those in column B.
| Column-A | Column-B |
|---|---|
| (i) Kharif crops | (a) Food for cattle |
| (ii) Rabi crops | b) Urea and super phosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung urine and plant waste |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (v)--------- | (e) Paddy and maize |
Sol:
(i) (e)
(ii) (d)
(iii) (b)
(iv)(c)
3. Give two examples of each
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
Sol:
(a) Examples of Kharif crop – maize and millets.
(b) Examples of Rabi crop – wheat and gram.
4. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing
Sol:
(a) Preparation of soil:
- Soil preparation includes breaking the soil, loosen it and turn it.
- Turning and loosening the soil brings nutrient rich soil to the top so that plants can use these nutrients.
- This also allows better root penetration, improve aeration, and integrate organic matter into the soil.
(b) Sowing:
- Sowing is the process of planting seeds into the soil to grow crops.
- It involves placing seeds in soil and nurturing them with water, light, and nutrients to allow them to sprout and grow into mature plants.
- For sowing, a funnel shaped tool is used. Nowadays, farmers use a seed drill for sowing seeds with the help of a tractor.
(c) Weeding:
- The undesirable plants which grow and compete with the crop’s plants for water, nutrients, space and light are called weeds.
- The removal of undesirable plants from the field is called weeding.
- Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light.
- Thus, they affect the growth of the crop.
- Some weeds interfere even in harvesting and may be poisonous for animals and human beings.
(d) Thresing:
- Threshing is the process of separating grain seeds from the chaff is called threshing.
- In threshing, the chaffs are beaten to free the grain seeds.
- Threshing can be done either manually or with the help of a machine.
5. Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Sol:
| Sl. No. | Fertilizer | Manure |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fertilizers is a man-made inorganic salt. | Manue is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung and plant residues. |
| 2. | Fertilzers is prepared in factories. | Manure can be prepared in the fields. |
| 3. | Fertilizers does not provide any humus to the soil. | Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil. |
| 4. | Fertilizers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. | Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients. |
6. What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Sol:
The supply of water to crops at regular intervals is called irrigation. Two methods of irrigation which conserve water are:
- Sprinkler System: This system is more useful on the uneven land where sufficient water is not available. This system contains a perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top which are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. The water comes out from the rotating nozzles on the crop as if it is raining. Sprinkler is very useful for lawns, coffee plantation and several other crops.
- Drip system: This system is used in those regions where availability of water is very poor. In this system, the water falls drop by drop directly near the roots. It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees.
7. If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Sol:
Wheat is a rabi crop. Hence it requires cold climatic conditions to be grown properly. If it is sown in the kharif season (June to October) then it will not grow properly or may even get destroyed due to due to high temperature, excess water etc.
8. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Sol:
Plants require nutrients for their proper growth and functioning. Continuous plantation of crops in a field makes the soil deficient in certain nutrients. This reduces the soil fertility and crop yield.
9. What are weeds? How can we control them?
Sol:
The undesirable plants which grow and compete with the crop’s plants for water, nutrients, space and light are called weeds. Examples of weed – crabgrass, chickweed etc.
- Tilling, Manual Methods and Use of Weedicides are the ways to remove weeds and control their growth.
- In Tilling, weeds are uprooted before sowing the crops.
- In Manual Methods, Khurpi is used to uproot or cutting them close to the ground from time to time.
- Weeds are also controlled by using certain chemicals called weedicides like 2, 4-D. These are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds.
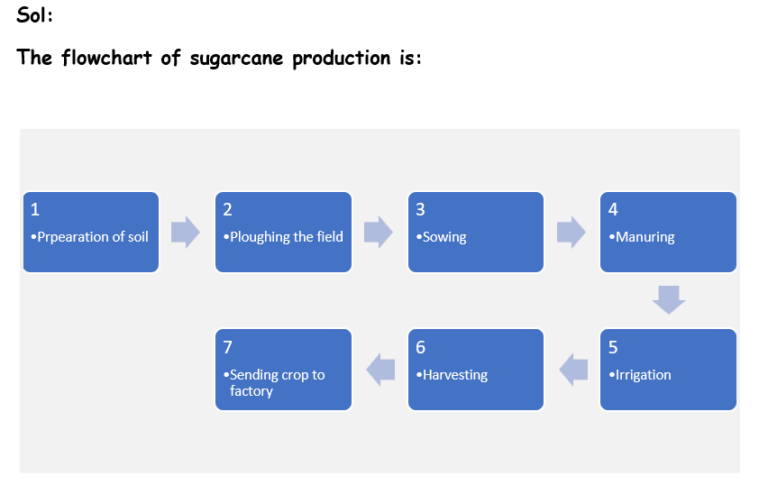
10. Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
Sending crop to sugar factory —- (1)
Irrigation —————————(2)
Harvesting ————————–(3)
Sowing ——————————(4)
Preparation of soil —————–(5)
Ploughing the field —————–(6)
Manuring ————————— (7)
11. Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from chaff.
Sol:
Down
1. Irrigation
2. Storage
5. Crop
Across
3. Harvester
4. Gram
5. Winnowing