NCERT Solutions-Class 8: Science: Coal and Petroleum
NCERT notes alongwith solutions for class 8 science “Coal and Petroleum” are provided here. The notes as well as solutions are very much helpful for the students to understand the topics. The solutions will be handy for quickly completing the homework and preparing for exams.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction: Coal and Petroleum
Natural resources are materials obtained from nature. Some are available in unlimited quantities, while others exist in limited amounts. Based on their availability, they are classified as:
- Inexhaustible Natural Resources – These resources are abundant and cannot be depleted by human activities.
- Examples: Sunlight, Air etc.
- Exhaustible Natural Resources – These resources have a limited supply and can be exhausted due to excessive use.
- Examples: Forests, Wildlife, Minerals, Coal, Petroleum, Natural Gas etc.
In this chapter, we will discuss some exhaustible natural resources such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas. These fuels were formed from the dead remains of living organisms (fossils) over millions of years, which is why they are called fossil fuels.
Coal
Carbonisation is the slow process of converting dead plant material into coal under high pressure and temperature over millions of years. This transformation occurs due to the decomposition of organic matter in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the formation of carbon-rich coal.
- Coal is a black or brownish-black sedimentary rock that is primarily composed of carbon.
- It is formed from the remains of plants that lived and died millions of years ago.

Formation of Coal
- Around 300 million years ago, dense forests in low-lying wetlands were buried under soil due to natural processes like flooding.
- As more soil deposited over them, they were compressed. The temperature also rose as they sank deeper and deeper. Under high pressure and high temperature, dead plants got slowly converted to coal.
- Since the coal was formed from the remains of vegetation, coal is also called a fossil fuel.
Uses of Coal
- Coal is processed in industry to get some useful products such as coke, coal tar and coal gas.
- Coal is used in railway engines to produce steam to run the engine.
- It is also used in thermal power plants to produce electricity.
Coke
- Coke is a hard, porous, and carbon-rich substance obtained by heating coal in the absence of air, a process known as destructive distillation.
- It is primarily used as a fuel and a reducing agent in metal extraction, especially in iron and steel production.
Properties of Coke
- High Carbon Content – Mostly pure carbon with minimal impurities.
- Porous and Hard – Provides structural support in blast furnaces.
- Burns with Less Smoke – More efficient than coal.
- Good Reducing Agent – Helps extract metals from their ores.
Uses of Coke
- In the Steel Industry – Used in blast furnaces to extract iron from its ore.
- As a Fuel – Burns efficiently with high heat output.
- In the Chemical Industry – Used in the production of calcium carbide, graphite, and ammonia.
Coal Tar
- Coal tar is a thick, black, viscous liquid obtained as a byproduct during the production of coke and coal gas from coal.
- Products obtained from coal tar are used as starting materials for manufacturing various substances like synthetic dyes, drugs, explosives, perfumes, plastics, paints, photographic materials, roofing materials, etc.
- Naphthalene balls, used as insect repellents, are also obtained from coal tar.
Coal Gas
- Coal gas is a flammable gaseous fuel made from coal. Coal gas is obtained during the processing of coal to get coke.
- It is used as a fuel in many industries situated near the coal processing plants.
Petroleum
- The world’s first oil well was drilled in Pennsylvania, USA, in 1859.
- In India, oil was first discovered in Makum, Assam, in 1867. Major oil reserves in India are found in Assam, Gujarat, Mumbai High, and the river basins of Godavari and Krishna.
- The word petroleum is derived from petra (rock) and oleum (oil) as it is mined from between the rocks under Earth.
- Petroleum is a dark oil liquid.
- Due to its great commercial importance, petroleum is also called ‘black gold’.

Formation of Petroleum
- Petroleum was formed from marine organisms.
- As these organisms died, their bodies settled at the bottom of the sea and got covered with layers of sand and clay.
- Over millions of years, absence of air, high temperature and high pressure. transformed the dead organisms into petroleum and natural gas.
Refining of Petroleum
- Refining of petroleum is the process of separating crude oil into useful products through fractional distillation.
- We obtained petroleum gas, petrol, diesel, lubricating oil, paraffin wax etc. through fractional distillation.
Process of Refining
- Heating – Crude oil is heated in a fractionating column.
- Separation – Different components get separated based on their boiling points.
- Collection – Various fractions are collected at different heights in the column.
Main Fractions Obtained
- Petroleum Gas – Used as LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas).
- Petrol (Gasoline) – Used as fuel for vehicles.
- Kerosene – Used in lamps and jet fuel.
- Diesel – Used in transport and industries.
- Lubricating Oil – Used in machinery and engines.
- Bitumen – Used in road construction and waterproofing.
Uses of Petroleum
- Fuel for Transportation – Used in the form of petrol, diesel, and aviation fuel for vehicles, ships, and airplanes.
- Cooking and Heating – LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) is used in homes and industries for cooking and heating.
- Electricity Generation – Some power plants use fuel oil or diesel to generate electricity.
- Industrial Uses – Petroleum is used in the manufacture of detergents, fibres (polyester, nylon, acrylic etc.), polythene and other man-made plastics.
- Lubrication – Lubricating oils derived from petroleum are used in machinery and engines to reduce friction.
- Road Construction – Bitumen, a petroleum byproduct, is used for paving roads and waterproofing.
- Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics – Many medicines, ointments, perfumes, and cosmetics contain petroleum-based ingredients.
| Sl. No. | Constituents | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Petroleum Gas in Liquid Form (LPG) | Fuel for home and industry |
| 2. | Petrol | Motor fuel, aviation fuel, solvent for dry cleaning |
| 3. | Kerosene | Fuel for stoves, lamps and for jet aircrafts |
| 4. | Diesel | Fuel for heavy motor vehicles, electric generators |
| 5. | Lubricating Oil | Lubrication |
| 6. | Paraffin Wax | Ointments, Candles, Vaseline etc. |
| 7. | Bitumen | Paints, road surfacing |
Natural Gas
- Natural gas is a clean-burning fossil fuel primarily composed of methane (CH₄).
- It produces less pollution than coal and oil.
- Natural gas is stored under high pressure as compressed natural gas (CNG).
Uses of Natural Gas
- Domestic Use – Used for cooking and heating in homes (LPG (Liquified Natural Gas) and PNG (Piped Natural Gas)).
- Electricity Generation – Used in gas-based power plants.
- Industrial Use – Powers factories, furnaces, and boilers.
- Fuel for Vehicles – Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) is used in cars, buses, and trucks.
- Fertilizer Production – Used in making ammonia and urea.
Preservation of some natural resources as well as environment
- drive at a constant and moderate speed as far as possible,
- switch off the engine at traffic lights or at a place where you have to wait,
- ensure correct tyre pressure.
- ensure regular maintenance of the vehicle.
Excercise
1. What are the advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels?
Sol:
The advantages of using CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) and LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) as fuels are:
- They burn with a smokeless flame thus reducing air pollution.
- They leave no ash or residue upon combustion, ensuring a cleaner environment.
- They are easy to handle, transport, and store safely.
2. Name the petroleum product used for surfacing of roads.
Sol:
Bitumen is used for surfacing of roads.
3. Describe how coal is formed from dead vegetation. What is this process called?
Sol:
Around millions of years ago, dense forests in low-lying wetlands were buried under soil due to natural processes like flooding. As more soil deposited over them, they were compressed. The temperature also rose as they sank deeper and deeper. Under high pressure and high temperature, dead plants got slowly converted to coal.
This whole process is called carbonisation.
4. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Fossil fuels are…………………, ……………………….. and ………………………
(b) Process of separation of different constituents from petroleum is called………………………
(c) Least polluting fuel for vehicle is………………
Sol:
(a) Coal, Petroleum and Natural Gas
(b) refining
(c) CNG (Compressed Natural Gas)
5. Tick True/False against the following statements.
(a) Fossil fuels can be made in the laboratory. (T/F)
(b) CNG is more polluting fuel than petrol. (T/F)
(c) Coke is almost pure form of carbon. (T/F)
(d) Coal tar is a mixture of various substances. (T/F)
(e) Kerosene is not a fossil fuel. (T/F)
Sol:
(a) False.
(Fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, and natural gas cannot be made in a laboratory because their formation requires millions of years under high pressure and temperature deep within the Earth’s crust.)
(b) False.
(CNG is less polluting than petrol. It burns more cleanly, producing lower levels of carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and particulate matter compared to petrol.)
(C) True.
(Coke is an almost pure form of carbon which is obtained by heating coal in the absence of air, a process known as destructive distillation. This removes impurities such as water, volatile gases, and tar, leaving behind carbon-rich substance.)
(D) Yes.
(Coal tar is a mixture of various substances. Coal Tar is obtained as a byproduct during the destructive distillation of coal.)
(E) False
(Kerosene is a fossil fuel because it is derived from crude oil which is formed from the remains of marine organisms over millions of years.)
6. Explain why fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources.
Sol:
Fossil fuels are exhaustible in nature because they are non-renewable resources that take millions of years to form, but are consumed at a much faster rate than they are replenished.
7. Describe characteristics and uses of coke.
Properties of Coke:
- High Carbon Content – Mostly pure carbon with minimal impurities.
- Porous and Hard – Provides structural support in blast furnaces.
- Burns with Less Smoke – More efficient than coal.
- Good Reducing Agent – Helps extract metals from their ores.
Uses of Coke:
- In the Steel Industry – Used in blast furnaces to extract iron from its ore.
- As a Fuel – Burns efficiently with high heat output.
- In the Chemical Industry – Used in the production of calcium carbide, graphite, and ammonia.
8. Explain the process of formation of petroleum.
Petroleum was formed from marine organisms. As these organisms died, their bodies settled at the bottom of the sea and got covered with layers of sand and clay. Over millions of years, absence of air, high temperature and high pressure. transformed the dead organisms into petroleum and natural gas.
9. The following Table shows the total power shortage in India from 1991–1997. Show the data in the form of a graph. Plot shortage percentage for the years on the Y-axis and the year on the X-axis.
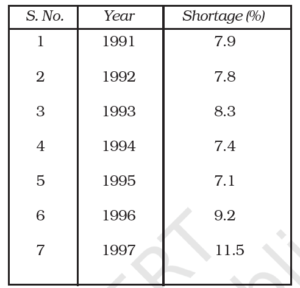
Sol: