NCERT-Solutions-Class 7: Science: Respiration in organism
NCERT notes along with solutions for class 7: science – Chapter “Respiration in organism” are provided here. The notes as well as solutions are very helpful for the students to understand the topic. The solutions will be handy for quickly completing the homework and preparing for exams.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction: Respiration in organisms
All living organism breathe. Human beings also do breathing. Do you know why we breathe?
Our body needs energy to perform various activities. We get the required energy through respiration. In respiration, we need oxygen to produce energy from the food stored in cells. To meet this requirement of oxygen we do breathing. During breathing, we take in air rich in “Oxygen” and take out air rich in “Carbon dioxide”. The air we take in is transported to all parts of the body and ultimately reaches each cell. In the cells, oxygen helps in the breakdown of food to release energy.
Do you know?
The use of the word “breathing” for “respiration” should be avoided. Breathing is a part of respiration. Not respiration at all. Let`s clear the difference.
Breathing means taking in air rich in oxygen and giving out air rich in carbon dioxide whereas respiration is a process in which the stored food (Glucose) is broken down in the cells which results in the release of energy.
Why cells need energy?
A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism. Each cell of an organism performs certain functions such as nutrition, transport, excretion and reproduction. To perform these functions, the cells need energy.
How the cells get energy?
During respiration, the food stored in the cells in the form of glucose reacts with oxygen and produces energy along with carbon dioxide and water.
Respiration
- Respiration is a chemical process in which the stored food (Glucose) is broken down in the cells which results in the release of energy.
- Since it takes place inside the cell, therefore, this process is also called cellular respiration
Types of respiration
There are two types of respiration.
- Aerobic Respiration
- Anaerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration
The word aerobic means in presence of oxygen. In aerobic respiration, the food (Glucose) is broken down into carbon dioxide and water using oxygen which results in the release of energy.
Let`s discuss in detail
All food molecules contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The food molecules are combined with oxygen. The process is called oxidation and the food is said to be oxidised. The process of oxidation converts the carbon to carbon dioxide (CO2) and the hydrogen to water (H2O) and, at the same time, sets free energy, which the cell can use in performing other activities. In the cells, the energy is not released all at once. The oxidation takes place in a series of small steps and each step releases some amount of energy.
Aerobic respiration can be summed up by the following equation –

Key Definition:-
Aerobic Respiration: – Aerobic respiration is a chemical process in cells that use oxygen to break down stored food (glucose) to release energy.Do you know:-
Indeed, it is in the mitochondria inside the cell where aerobic respiration takes place. The mitochondria generate a compound called ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), also called energy currency of the cell, which is used by the cell as the source of energy for driving other chemical reactions in the cytoplasm and nucleus.Anaerobic respiration
- The word anaerobic means ‘in the absence of oxygen’.
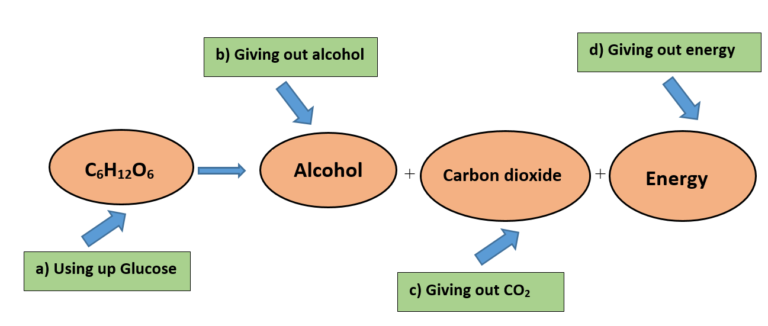
- In anaerobic respiration, the stored food (Glucose) is broken down into alcohol and carbon dioxide in the absence of oxygen which results in the release of small amount of energy.
- A common example is the Yeasts. Yeasts are a single celled-organisms. They respire anaerobically and during that process yield alcohol.
Anaerobic respiration can be summed up by the following equation –
Anaerobic respiration in human body
- Our muscle cells can also respire anaerobically, but only for a short time, when there is a temporary deficiency of oxygen.
- During vigorous physical activity such as fast running, cycling, walking for many hours or heavy weight lifting, the demand for energy is high. However, the supply of oxygen to produce the energy is limited. Then anaerobic respiration takes place in the muscle cells to fulfil the demand for energy. The products are, however, different from those produced by anaerobic respiration in yeast.
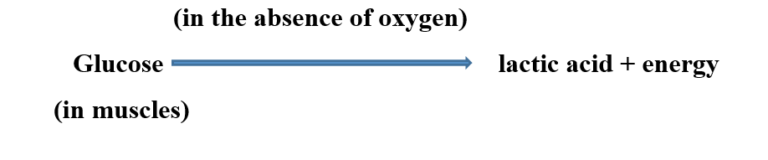
- The lactic acid builds up in the muscles and causes muscle fatigue (cramp). We get relief from cramps after a hot water bath or a massage. Can you guess why it is so? Hot water bath or massage improves circulation of blood. As a result, the supply of oxygen to the muscle cells increases. The increase in the supply of oxygen results in the complete breakdown of lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water.
Difference between Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration
| Key Concept | Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Requirement | It takes place in the presence of oxygen | It takes place in the absence of oxygen |
| Location | It takes place in cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria | It takes place in cytoplasm only |
| Energy Yield | High amount of energy is released. 38 ATP molecules is produced | Small amount of energy is released. Only 2 ATP molecules is produced. |
| End Product | Glucose reacts with oxygen to release energy alongwith carbon dioxide and water. | Glucose break down to give carbon dioxide, alcohol and energy. |
| Oxidation of Glucose | Complete oxidation of glucose | Incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place as glucose is partially broken down. |
| Examples | Higher organism like animals | Lower organism like bacteria, yeasts etc. and muscles of animals |
Breathing
Breathing involves two stages – (i) Inspiration (ii) Expiration
(i) Inspiration – During inspiration, the atmospheric air which is rich in oxygen is taken in. The process of taking in air rich in oxygen into the body is called inhalation.
(ii) Expiration – During expiration, the alveolar air which is rich in carbon dioxide is released out from the body. The process of releasing out air rich in carbon dioxide from the body is called exhalation.
Key Points:-
• The number of times a person breathes in a minute is called breathing rate.• Rate of breathing changes according to the requirement of oxygen by the body under different physical activity.
• The normal breathing rate of a person ranges between 12 and 18 breathes per minute.
• During heavy exercise the breathing rate can increase upto 25 times per minute
• A breathe means one inhalation and one exhalation.
Human respiratory system
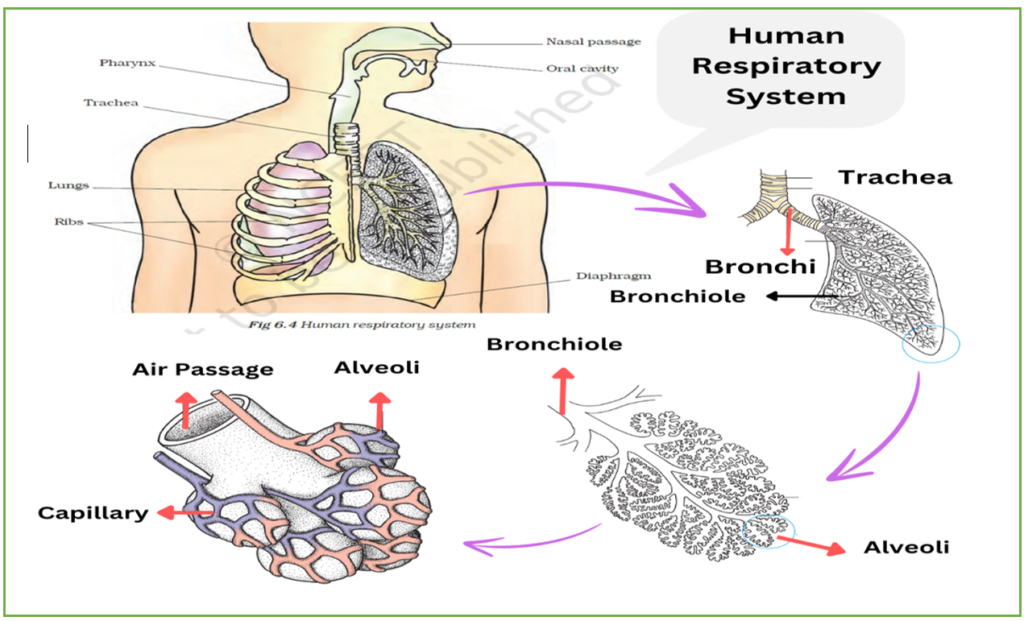
Human respiratory system starts from the nostrils opening out above the upper lips. It leads to a nasal chamber through the nasal passage. The nasal chamber opens into the pharynx. The pharynx opens through the larynx region, a cartilaginous box helps in sound production, into the trachea. The trachea is divided into two smaller tubes called bronchi (plural-bronchi, singular-bronchus) which enter the lungs.
Each bronchus divides into secondary bronchi, then into tertiary bronchi, which in turn divide, creating smaller and smaller diameter called terminal bronchioles. The terminal bronchioles connect to several very thin, irregular-walled and vascularised bag-like structures called alveoli. The branching network of bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli comprise the lungs.
How do we breathe
Let’s discuss the mechanism of breathing.
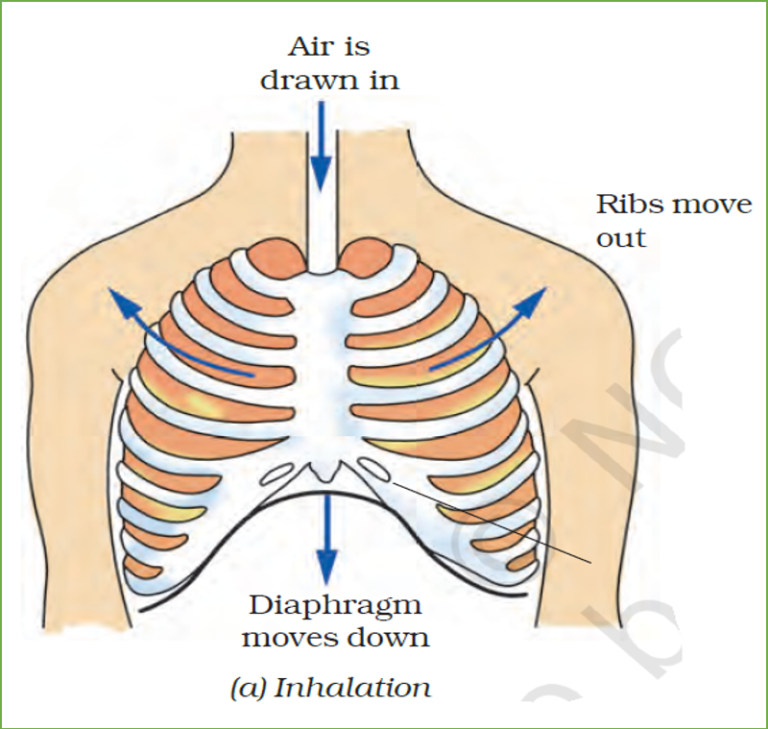
When we breathe the air enters the nose and moves to the nasal cavity. After passing through the nasal cavity, the air enters the pharynx. Then it goes into the trachea or the windpipe. From the trachea, the air enters the lungs through the bronchi. Lungs are present in the chest cavity (thoracic cavity). This cavity is surrounded by ribs on the sides. A large, muscular sheet called a diaphragm forms the floor of the chest cavity. Breathing involves the movement of the diaphragm and the rib cage.
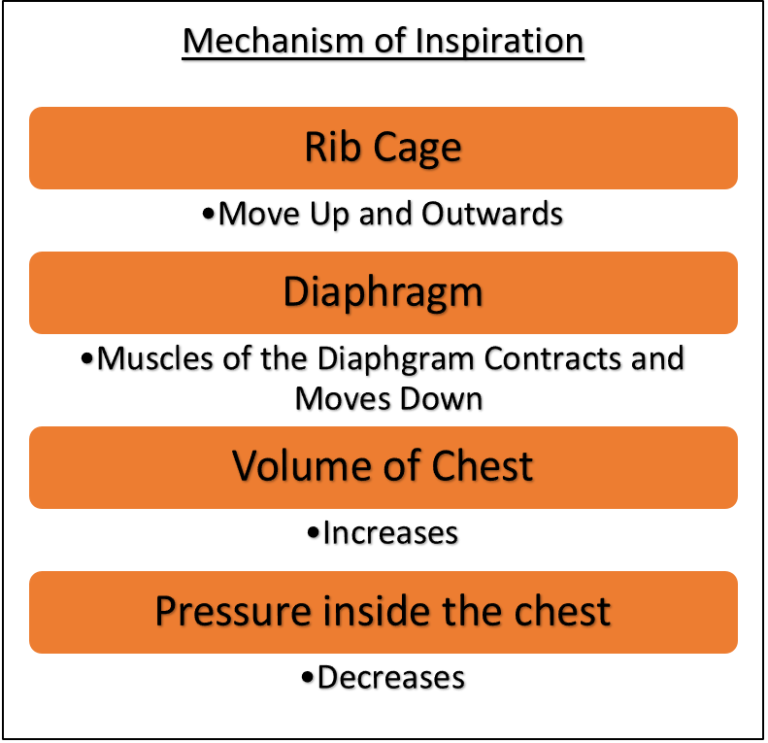
During inhalation, ribs and sternum move up and outwards and the diaphragm moves down. This movement increases space in our chest cavity and thus decreases the pressure. As a result, the air outside the body flows into the lungs due to the pressure gradient i.e. air flows from high pressure to low pressure.
Key Concept
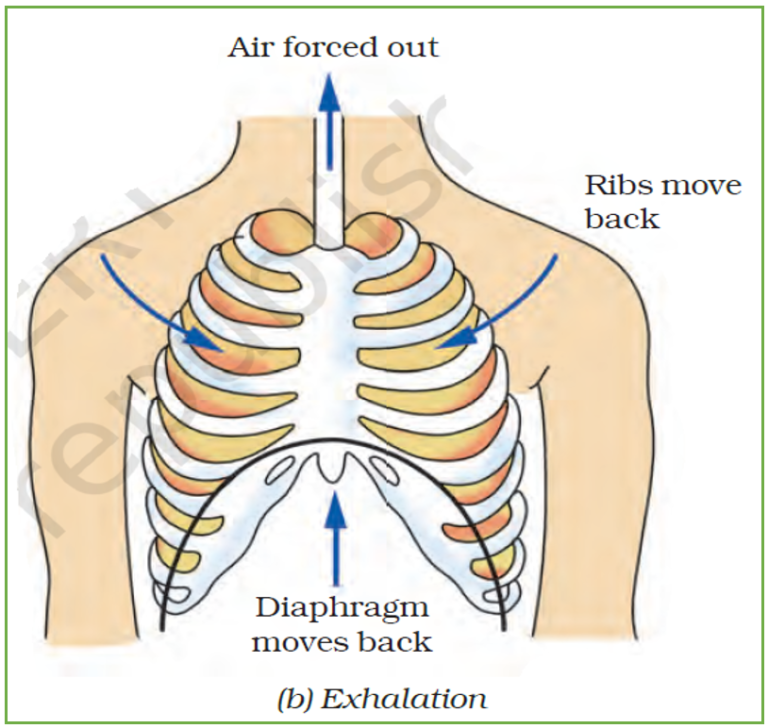
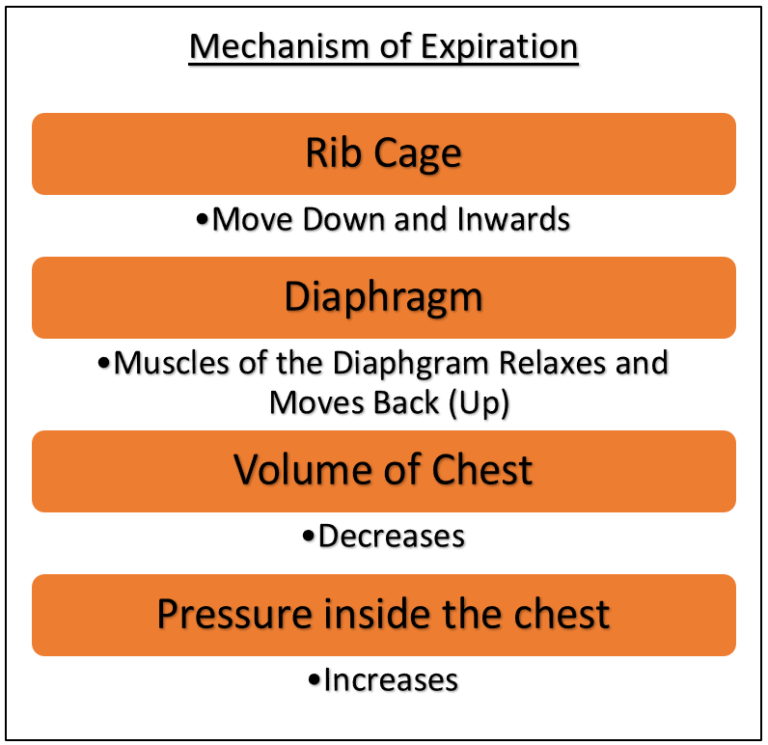
During exhalation, ribs and sternum move down and inwards, while the diaphragm relaxes and moves up to its former position. This reduces the size of the chest cavity and thus increases the pressure. As a result, the air is pushed out of the lungs due to the pressure gradient.
Key Concept
Solution of the exercise
Q1. Why does an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race?
Ans:
This phenomenon is called post-exercise oxygen consumption, also known as oxygen-debt. When an athlete runs a race, his body requires high amount of energy, but the supply of oxygen to produce that energy is limited. To meet up this energy need, muscle cells undergo anaerobic respiration which produces lactic acid in the body. And when an athlete breathes faster and deeper, the oxygen reacts with lactic acid to form carbon dioxide and water and releases the rest of the energy originally in the glucose.
Q2. List the similarities and differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Ans:
Similarities:
1. Energy is released in both types of respiration.
2. Carbon dioxide is produced as a by-product.
3. Both take place inside the cell.
Differences
| Key Concept | Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Requirement | It takes place in the presence of oxygen | It takes place in the absence of oxygen |
| Location | It takes place in cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria | It takes place in cytoplasm only |
| Energy Yield | High amount of energy is released. 38 ATP molecules is produced | Small amount of energy is released. Only 2 ATP molecules is produced. |
| End Product | Glucose reacts with oxygen to release energy alongwith carbon dioxide and water. | Glucose break down to give carbon dioxide, alcohol and energy. |
| Oxidation of Glucose | Complete oxidation of glucose | Incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place as glucose is partially broken down. |
| Examples | Higher organism like animals | Lower organism like bacteria, yeasts etc. and muscles of animals |
Q3. Why do we often sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust-laden air?
Ans:
Sneezing is a method through which our body tries to expel unwanted dust particles out from our body. When dust particles enter our nostril it triggers a message to the brain. The brain instructs the nasal chamber to initiate sneezing.
Q4. Take three test-tubes. Fill ¾th of each with water. Label them A, B and C. Keep a snail in test-tube A, a water plant in test-tube B and in C, keep snail and plant both. Which test-tube would have the highest concentration of CO2?
Ans:
Test Tube A – This test tube will have the highest carbon dioxide concentration because the snail releases carbon dioxide through respiration.
Test Tube B – Plant will take in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and releases oxygen in the test tube. So the concentration of carbon dioxide will be least.
Test Tube C – In this test tube, the carbon dioxide released by the snail will be utilized by the plant for photosysthesis and will release oxygen.
Q5. Tick the correct answer:
Answer:
(a) In cockroaches, air enters the body through
(i) lungs (ii) gills (iii) spiracles (iv) skin
(b) During heavy exercise, we get cramps in the legs due to the accumulation of
(i) carbon dioxide (ii) lactic acid (iii) alcohol
(iv) water
(c) Normal range of breathing rate per minute in an average adult person at rest is:
(i) 9–12 (ii) 15–18 (iii) 21–24 (iv) 30–33
(d) During exhalation, the ribs
(i) move outwards (ii) move downwards
(iii) move upwards (iv) do not move at all
Q6. Match the items in Column I with those in Column II:
Match the items in Column I with those in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| (a) Yeast | (i) Earthworm |
| (b) Diaphgram | (ii) Gills |
| (c) Skin | (iii) alcohal |
| (d) Leaves | (iv) Chest cavity |
| (e) Fish | (v) Stomata |
| (f) Frogs | (vi) Lungs and Skin |
| — | (vii) Trachae |
Ans:
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| (a) Yeast | (iii) Alcohal |
| (b) Diaphgram | (iv) Chest Cavity |
| (c) Skin | (i) Earthworm |
| (d) Leaves | (v) Stomata |
| (v) Fish | (ii) Gills |
| (f) Frogs | (vi) Lungs and Skin |
Q7. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(i) During heavy exercise the breathing rate of a person slows down. (T/F)
(ii) Plants carry out photosynthesis only during the day and respiration only at night. (T/F)
(iii) Frogs breathe through their skins as well as their lungs. (T/F)
(iv) The fishes have lungs for respiration. (T/F)
(v) The size of the chest cavity increases during inhalation. (T/F)
Ans:
(i) During heavy exercise the breathing rate of a person slows down – False. Explanation – The breathing rate of a person increases during heavy exercise.
(ii) Plants carry out photosynthesis only during the day and respiration only at night. – False.
Explanation – Plants carry out photosynthesis only during the day but respiration takes place throughout the day and night.
(iii) Frogs breathe through their skins as well as their lungs – True.
(iv) The fishes have lungs for respiration – False.
Explanation – The fishes have gills for respiration.
(v) the size of the chest cavity increases during inhalation – True.
8. Given below is a square of letters in which are hidden different words related to respiration in organisms. These words may be present in any direction — upwards, downwards, or along the diagonals. Find the words for your respiratory system. Clues about those words are given below the square.
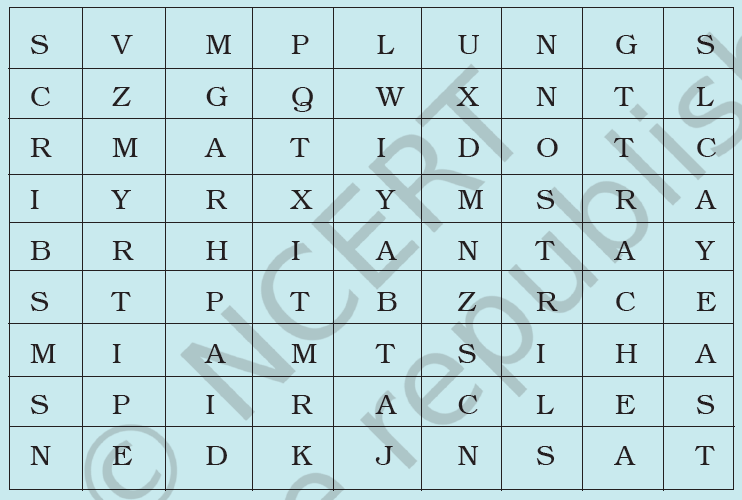
(i) The air tubes of insects
(ii) Skeletal structures surrounding chest cavity
(iii) Muscular floor of chest cavity
(iv) Tiny pores on the surface of leaf
(v) Small openings on the sides of the body of an insect
(vi) The respiratory organs of human beings
(vii) The openings through which we inhale
(viii) An anaerobic organism
(ix) An organism with tracheal system
Ans:
(i) Trachea
(ii) Ribs
(iii) Diaphragm
(iv) Stomata
(v) Spiracles
(vi) Lungs
(vii) Nostrils
(viii) Yeast
(ix) Ant
9. The mountaineers carry oxygen with them because: (a) At an altitude of more than 5 km there is no air. (b) The amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground. (c) The temperature of air is higher than that on the ground. (d) The pressure of air is higher than that on the ground.
Ans:
(b) The amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground.