NCERT-Solutions-Class 7: Science: Physical and Chemical Changes
NCERT notes along with solutions for class 7: science – Chapter “Physical and Chemical Changes” are provided here. The notes as well as solutions are very much helpful for the students to understand the topic. The solutions will be handy for quickly completing the homework and preparing for exams.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction: Physical and Chemical Changes
You notice several changes in your surroundings every day. One or more substances may be involved in these changes like boiling an egg, ripping paper, souring milk, stretching rubber bands, adding sugar to water to make a drink etc.
Task-1: Make a list of 10 changes that you have noticed around you
- Melting of Ice
- Evaporation of water
- Melting of wax
- Ripening of fruits
- Rusting of iron
- Adding salt and lemon to water
- Crushing a CAN
- Igniting a match stick
- Chopping of wood
- Burning of paper
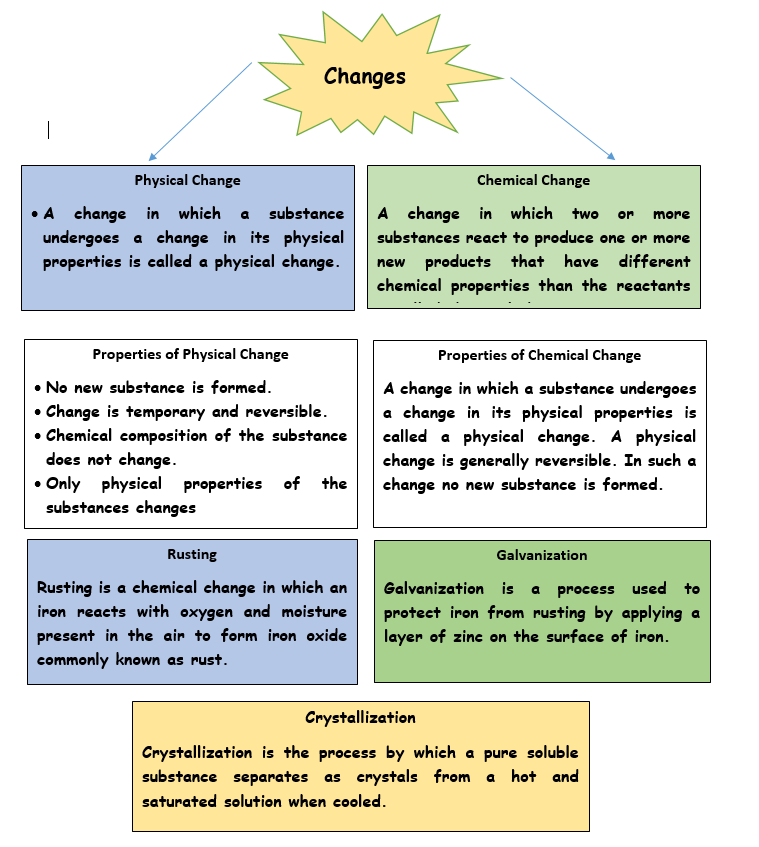
Physical Change
- A change in which a substance undergoes a change in its physical properties is called a physical change.
- A physical change is generally reversible. In such a change no new substance is formed.
- The physical properties of a substance are: shape, size, colour and state of a substance.
Properties of Physical Change
- No formation of new substance – During a physical change, no new substance is formed.
- Reversibility:- A physical change is usually temporary and reversible in nature. But in certain cases, the change is irreversible.
- Chemical Composition:- In a physical change, the chemical composition of the substance does not change.
- Physical Properties:- In a physical change, the physical properties such as colour, shape and size of a substance may undergo a change.
- Energy Changes: During physical changes, energy can be either absorbed or released, but the chemical composition of the substance remains unchanged. Energy changes are usually related with changes in the state of matter or physical qualities like:
a. Melting – Solid to liquid —- Energy absorbed
b. Freezing — liquid to solid — Energy released
c. Evaporation — liquid to gas — Energy absorbed
d. Condensation — gas to liquid — Energy released

Activity- 5.1
Cut a piece of paper in four square pieces. Cut each square piece further into four square pieces. Lay these pieces on the floor or a table so that the pieces acquire the shape of the original piece of paper (Fig. 5.1). Obviously, you cannot join the pieces back to make the original piece, but is there a change in the property of the paper?
Ans:
Yes, there is an irreversible physical change in the property of the paper. The size of the paper has been changed to four small pieces.
Activity- 5.2
Collect the chalk dust lying on the floor near the chalkboard in your classroom. Or, crush a small piece of chalk into dust. Add a little water to the dust to make a paste. Roll it into the shape of a piece of chalk. Let it dry. Did you recover chalk from the dust?
Ans:
Yes. We can recover chalk from its dust. This type of change is a reversible physical change.
Activity- 5.3
Take some ice in a glass or plastic tumbler. Melt a small portion of ice by placing the tumbler in the sun. You have now a mixture of ice and water. Now place the tumbler in a freezing mixture (ice plus common salt). Does the water become solid ice once again?
Ans:
No. The water will not become solid ice once again at 0 degree Celsius because the salt present in the mixture lowers down the freezing point of the water.
Activity- 5.4
Boil some water in a container. Do you see the steam rising from the surface of the water? Hold an inverted pan by its handle over the steam at some distance from the boiling water. Observe the inner surface of the pan. Do you see any droplets of water there?
Ans:
Yes, we can see droplets of water there. We know that the water vapour (steam) starts cooling down as it rises above. At certain height, the steam cools down enough and condenses into water droplets. In this case also, when the steam comes in contact with the cooled surface of the inverted pan which is kept at some distance. It cools down enough to form a water droplet on the inner surface of the pan.
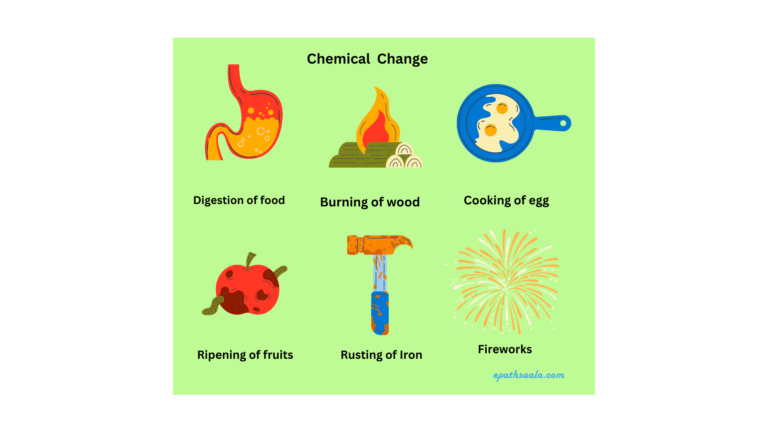
Chemical Change
- A change in which two or more substances react to produce one or more new products that have different chemical properties than the reactants is called chemical change.
- A chemical change is also known as a chemical reaction.
- A chemical change is mostly Irreversible. In a chemical reaction, the substances which react are called reactants and the new substance formed as a result of chemical reaction is called the product.

Properties of Chemical Change
- Formation of new substance – New substances having different chemical properties are formed as a result of chemical change.
- Energy Changes:- Chemical changes are frequently accompanied by energy changes, such as heat, light, or sound. These changes might be either exothermic (energy release) or endothermic (energy absorption).
- Irreversibility:- Most chemical changes are difficult to reverse without a subsequent chemical reaction.
- Chemical Composition: In a chemical change, the composition of the substance changes to form a new substance.
In addition to these, a chemical change may also accompany the following:
- Heat, light or any other radiation (ultraviolet, for example) may be given off or absorbed.
- Sound may be produced.
- A change in smell may take place or a new smell may be given off.
- A colour change may take place
- A gas may be formed.
Difference between Physical and Chemical Change
| Key Concept | Physical Change | Chemical Change |
|---|---|---|
| Nature of Change | It involves a change in the physical properties of a substance without changing its chemical composition. These changes generally affect the form or state of the material | It involves a change in the chemical composition of the substance. These changes result in the creation of new substances with different chemical propeties |
| Energy Changes | Energy can be either absorbed or released. Energy changes are usually related to changes in the state of matter or physical qualities | Chemical changes are frequently accompanied by energy changes, such as heat, light, or sound. These changes might be either exothermic (energy release) or endothermic (energy absorption). |
| Reversibility | Physical changes are generally reversible. | Chemical changes are usually irreversible under normal conditions. |
| Formation of new substance | No new substance is formed. The substance remains the same. Only the state of the substance changes. | A new substance is formed with new chemical properties. |
Activity- 5.6(A)
Get a small piece of a thin strip or ribbon of magnesium. Clean its tip with sandpaper. Bring the tip near a candle flame. It burns with a brilliant white light. When it is completely burnt it leaves behind a powdery ash. Does the ash look like the magnesium ribbon?
Ans:
No. the ash will not look like the magnesium ribbon because the magnesium after burning becomes a different magnesium oxide.
The chemical equation is:
Activity- 5.6(B)
Collect the ash (Magnesium Oxide) and mix it with a small amount of water. Stir the mixture (aqueous solution) well. Test the mixture with blue and red litmus papers. Does the mixture turn red litmus blue? Does the mixture turn blue litmus red? On the basis of this test, how do you classify the aqueous solution — acidic or basic?
Ans:
When the Magnesium Oxide (Ash) is dissolved in water, a new substance Magnesium Hydroxide is formed which is alkaline (basic) by nature as shown in the given chemical reaction.
Magnesium oxide (MgO) + Water (H2O) → Magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)2]
- when the red litmus is added to the solution of Magnesium hydroxide, the colour of the red litmus turns blue because the basic solution turns red litmus into blue colour.
- when blue litmus is added to the solution of Magnesium Hydroxide, the colour of the blue litmus will not change.
Activity- 5.7
Dissolve about a teaspoonful of copper sulphate (blue vitriol or neela thotha) in about half a cup of water in a glass tumbler or a beaker. Add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to the solution. Drop a nail or a used shaving blade into the remaining solution. Do you see any change in the colour of the solution? Take out the nail or the blade. Has it changed in any way?
Ans:
When a nail or shaving blade is put in the solution of Copper Sulphate (Blue Vitriol or Neela Thota). The copper sulphate reacts with Iron. As a result, the colour of the solution turns to green from blue due to the formation of Iron Sulphate. And the brown deposit on the nail/ shaving blade is copper.
Copper sulphate solution (blue vitrol) + Iron → Iron sulphate solution (green) + Copper (brown deposit)
Rusting of an Iron
- Rusting is a chemical process in which Iron reacts with air and water and form a brownish layer on its surface.
- Rust is an iron oxide and a form of corrosion.
- For rusting, the presence of both oxygen and water (or water vapour) is essential.
The process of rusting can be presented by the following equation:
Iron (Fe) + Oxygen (O2, from the air) + water (H2O) → rust (iron oxide Fe2O3)
Prevention of iron from rusting
Iron can be prevented from rusting through the following ways:
- By applying a coat of paint or grease.
- Galvanization is another method of protecting Iron from rusting by applying a layer of metal like chromium or zinc on Iron.
Galvanisation
Galvanisation is a process used to protect iron from rusting by applying a layer of zinc or chromium on the surface of iron.
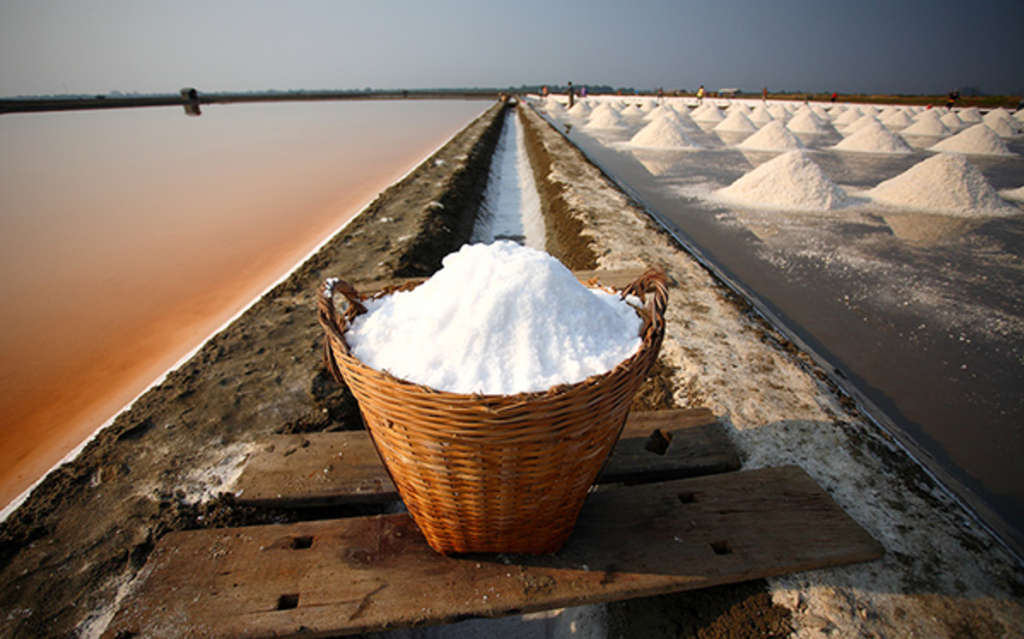
Crystallization:
- Crystallisation is the process by which a pure soluble substance separates as crystals from a hot and saturated solution when cooled.
- In simple words, it is a purification technique that separates a solid from its solution.
- This procedure is used to separate pure common salt from impure common salt collected from the sea.

Key Concept
Solution of the exercise
Q1. Classify the changes involved in the following processes as physical or chemical changes:
1. Photosynthesis2. Dissolving sugar in water
3. Burning of coal
4. Melting of wax
5. Beating aluminium to make aluminium foil
6. Digestion of food
Sol:-
1. Photosynthesis – Chemical Change
Explanation:-In photosynthesis process, water and carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll undergo a chemical reaction and forms two new substances-glucose and oxygen. The formula for this reaction is given below:
6CO2+6H2O⟶C6H12O6+6O2
2. Dissolving Sugar in water – Physical Change
Explanation:-When we dissolve sugar in water. No new substance is formed. Only the state of the substance changes to liquid from solid form. We can get sugar by vapourising the water of the solution.
Sol:-
3. Burning of Coal – Chemical Change
Explanation:-During burning the carbon in coal reacts with atmospheric oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and ash with release of energy (exothermic reaction).
C + O2 → CO2 + Ash
4. Melting of wax – Physical Change
Explanation:-Melting of wax involves only a change of state from solid to liquid. In this process, no new substance is produced. Only the physical properties i.e. its form of state changes.
5. Beating aluminium to make aluminium foil – Physical Change
Explanation:-Beating aluminium to make aluminium foil is a physical change because it involves only physical change i.e. lessening the thickness of the aluminium. In this process, the chemical properties of the aluminium remain intact.
6. Digestion of food – Chemical Changes
Explanation:-During digestion, the food is chemically digested with the action of various enzymes present in our body. In this process, new substances are formed which are different from their original substance.
2. State whether the following statements are true or false. In case a statement is false, write the corrected statement in your notebook. (a) Cutting a log of wood into pieces is a chemical change. (True/False) (b) Formation of manure from leaves is a physical change. (True/False) (c) Iron pipes coated with zinc do not get rusted easily. (True/False) (d) Iron and rust are the same substances. (True/False) (e) Condensation of steam is not a chemical change. (True/False)
Sol:-
a) Cutting a log of wood into pieces is a chemical change – False
Correct Statement – Cutting a log of wood into pieces is a physical change.
Explanation – In this process, no new substance is formed. Only the physical properties i.e. the size is reduced to small pieces.
b) Formation of manure from leaves is a physical change – False
Correct Statement – Formation of manure from leaves is a chemical change.
Explanation – In this process, a new substance i.e. manure is formed from the leaves.
Sol:-
c) Iron pipes coated with zinc do not get rusted easily – True.
Explanation – Coating of zinc prevents iron from coming into contact with oxygen and moisture from its surrounding environment. Consequently, protect it from rusting.
d) Iron and rust are the same substances – False
Correct Statement – Iron and rust are different substances.
Explanation – Iron is a metal. The chemical formula for iron is Fe. Whereas rust is an iron oxide. When iron comes in contact with oxygen and moisture of its surrounding environment. It forms rust. Its chemical formula is Fe2O3. Hence, iron is different from rust.
e) Condensation of steam is not a chemical change – True.
Explanation – When water is heated, it turns into water vapour (steam) and when steam is condensed, it turns into water droplets. Throughout this process, only the state of water changes; no new substance is formed. As a result, we can conclude that condensation of steam does not include any chemical changes.
3. Fill in the blanks in the following statements:
(a) When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, it turns milky due to the formation of _________.
(b) The chemical name of baking soda is _________.
(c) Two methods by which rusting of iron can be prevented are _________ and _________.
(d) Changes in which only _________ properties of a substance change are called physical changes.
(e) Changes in which new substances are formed are called _________ changes.
Sol:-
a) Calcium Carbonate
b) Sodium Bicarbonate or Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
c)Painting and Galvanization
d) Physical
e) Chemical
4. When baking soda is mixed with lemon juice, bubbles are formed with the evolution of a gas. What type of change is it? Explain.
Sol:-
Mixing baking soda (Sodium bicarbonate) with lemon juice (citric acid) results in the formation of bubbles and the release of carbon dioxide gas. This reaction produces a new substance, called carbon dioxide which indicates it is a chemical change.
Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3) + Citric acid —— CO2 (evolved) + other substance
5. When a candle burns, both physical and chemical changes take place. Identify these changes. Give another example of a familiar process in which both the chemical and physical changes take place.
Burning a candle involves both melting and burning of wax causing physical and chemical changes.
a) Melting of wax – physical changes
b) Burning of wax – chemical changes
Another example in which both the physical and chemical changes take place is the digestion of food.
a) Chewing of food breaks down big food particles into smaller ones causing physical changes.
b) After entering the stomach, food particles undergo chemical changes as enzymes aid in the digestion of smaller food particles.
Q.6 How would you show that the setting of curd is a chemical change?
Sol:-
Once created, the curd cannot be used to make milk again. Curd is a new substance that differs from milk in terms of taste, smell and other chemical properties. Hence, we can say that the setting of curd is a chemical change.
7. Explain why burning of wood and cutting it into small pieces are considered as two different types of changes.
Burning of wood and cutting of wood into small pieces are considered as chemical change and physical change respectively. Let`s discuss it in detail.
1. Burning of wood – Chemical change – A new substance (charcoal) is obtained. This change is irreversible.
Wood + Oxygen → Charcoal + Carbon dioxide + Heat + Light
2. Cutting of wood – Physical change – No new substance is formed. Only the shape and size are changed. No change in chemical properties.
8. Describe how crystals of copper sulphate are prepared.
- The crystals of copper sulphate are obtained by the process of Crystallization.
- In this procedure, a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid are added to water. The water is then boiled.
- Now add copper sulphate powder in the boiling water with stirring. The powder is added until the solution becomes saturated.
- Afterwards, it is filtered into a china dish, allowed to cool, and kept undisturbed.
- After some time the crystals of copper sulphate separate out.
9. Explain how the painting of an iron gate prevents it from rusting.
- Rusting is a type of corrosion in which an iron reacts with the oxygen and moisture of its surroundings and forms a layer of iron oxide on its surface.
- To prevent an iron gate from rusting a coating of paint (zine/chromium) is generally applied so that the surface of iron does not directly come in contact with oxygen and moisture.
- In this way, an iron gate can be prevented from rusting.
10. Explain why rusting of iron objects is faster in coastal areas than in deserts.
Rusting of iron occurs only if iron comes in contact with oxygen and moisture in its surroundings. The air of coastal areas contains a high percentage of moisture because of sea or ocean, whereas in deserts the air is generally dry and hot. As the percentage of moisture in air is higher in coastal areas compared to desert areas, the rusting becomes faster.
11. The gas we use in the kitchen is called liquified petroleum gas (LPG). In the cylinder it exist as a liquid. When it comes out from the cylinder it becomes a gas (Change – A) then it burns (Change – B). The following statements pertain to these changes. Choose the correct one. (i) Process – A is a chemical change. (ii) Process – B is a chemical change. (iii) Both processes A and B are chemical changes. (iv) None of these processes is a chemical change.
Sol:-
(ii) Process – B is a chemical change.
12. Anaerobic bacteria digest animal waste and produce biogas (Change – A). The biogas is then burnt as fuel (Change – B). The following statements pertain to these changes. Choose the correct one. (i) Process – A is a chemical change. (ii) Process – B is a chemical change. (iii) Both processes A and B are chemical changes. (iv) None of these processes is a chemical change.
Sol:-
(iii) Both processes A and B are chemical changes.