Nutrition in Plants-Class 7-Science-NCERT solutions
NCERT notes alongwith solutions for class 7 science “Nutrition in Plants” are provided here. The notes as well as solutions are very much helpful for the students to understand the topics. The solutions will be handy for quickly completing the homework and preparing for exams.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are Nutrients?
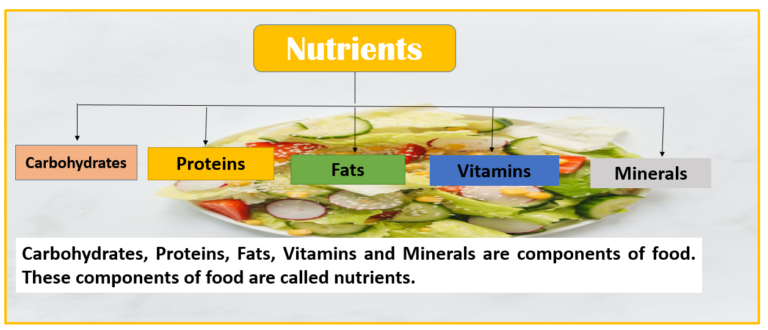
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Fats, Vitamins and Minerals are components of food. These components of food are called nutrients.
What is nutrition?
Nutrition is the mode of taking food by an organism and its utilisation by the body.
Modes of Nutrition
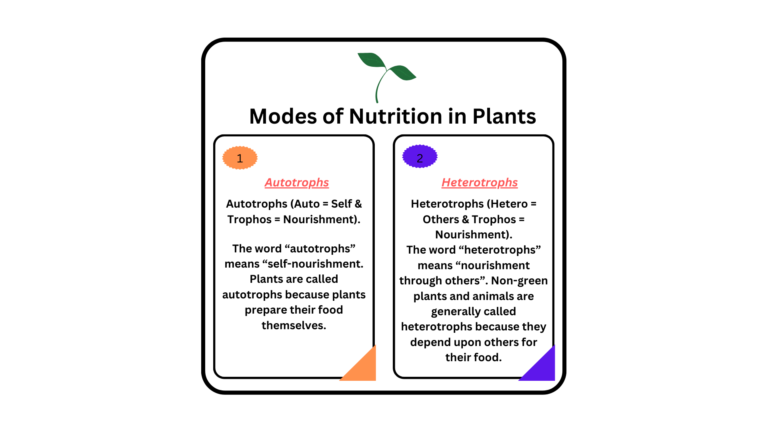
There are two modes of nutrition – Autotrophs and Heterotrophs.
- Autotrophs: The term “Autotrophs” is made from two words ‘Auto’ means – ‘Self’ and ‘Troph’ means – ‘Nutrition’. Thus, the mode of nutrition in which organisms make food themselves from simple substances is called autotrophic nutrition. For example – plants.
- Heterotrophs: The term “Heterotrophs” is made from two words ‘Hetero’ means – ‘Other’ and ‘Troph’ means – ‘Nutrition’. Hence, the mode of nutrition in which organisms take in food prepared by others is called heterotrophic nutrition. For example – Animals and other organisms.
Why nutrients are necessary for us?
Nutrients are necessary for our body because they help:
- to enable living organisms to build their bodies.
- to grow
- to repair damaged parts of their bodies.
- to provide energy to carry out life processes.

Photosynthesis: Food-making process in plants
- The term “Photosynthesis” is made from two words: Photo (=light) and Synthesis (= to combine).
- It is a process by which green plants prepare their food in the presence of sunlight.
- Chlorophyll, Water, Carbon dioxide and Sunlight are the raw materials necessary to carry out the process of photosynthesis.
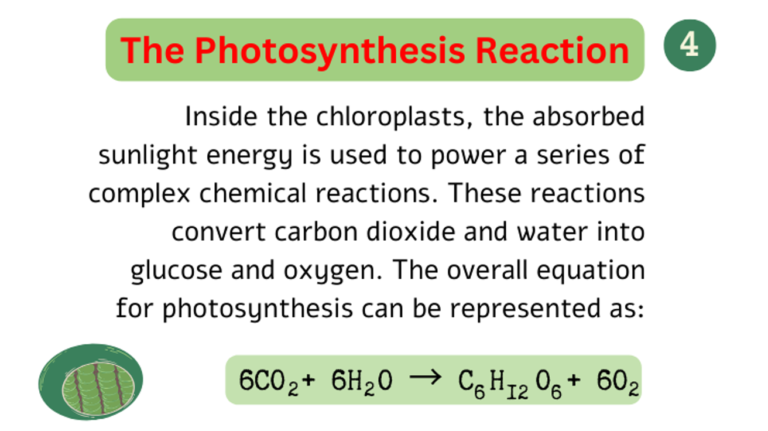
- During photosynthesis, chlorophyll containing cells of leaves in the presence of sunlight, use carbon dioxide and water to synthesise carbohydrates. The process can be represented as:
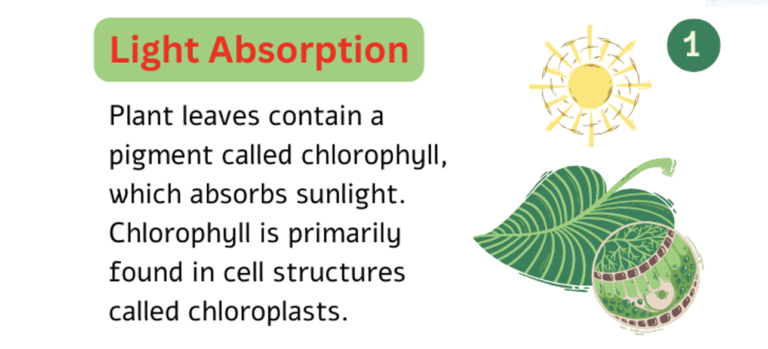


Chlorophyll
- The leaves of a plant contain a green pigment called chlorophyll.
- It helps leaves to capture the sunlight. This energy is used to synthesise (prepare) food from carbon dioxide and water.

Why algae are green in colour?

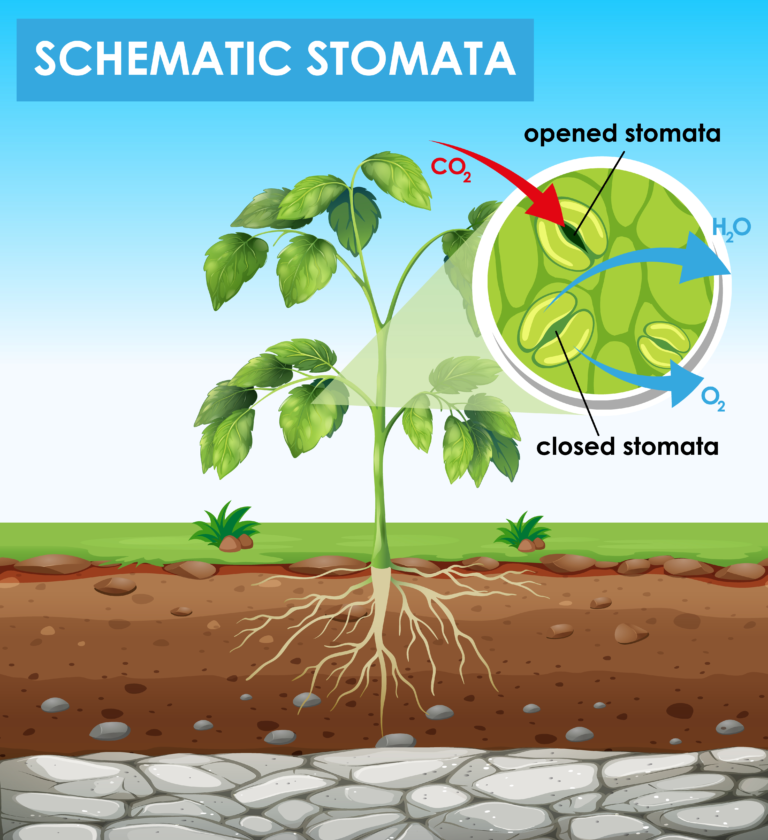
Stomata
- Stomata are small pores found on the surface of leaves as well as stems of plants.
- The main function of the stomata is to let in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere for photosynthesis.
Synthesis of plant food other than carbohydrates
Besides carbon dioxide, plants can also synthesize other food components like proteins and fats. Plants synthesize proteins from nitrogen. The soil contains certain bacteria that convert gaseous nitrogen into a usable form and release it into the soil. The plants along with water absorb these nitrogen.
Other Modes of Nutrition in Plants
There are some plants which do not have chlorophyll. They cannot synthesise food. Such plants depend on the food produced by other plants. They use the heterotrophic mode of nutrition. Based on their mode of nutrition, plants are classified into the following groups:
- Parasitic Plants
- Insectivorous Plants
- Saprophytic Plants
- Symbiotic Plants
Parasitic Plants
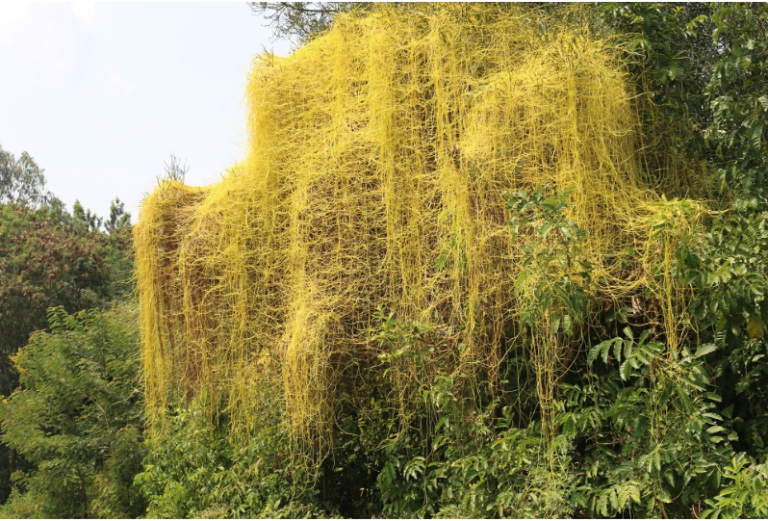
Parasitic plants live on or inside other living plants, called host, in order to obtain food from the host plants. The host plant does not get any benefit from the parasitic plants. For example – Cuscuta (Amarbel). Cuscuta is a yellow tubular plant. It does not have chlorophyll. It takes readymade food from the plant on which it climbs. It deprives the host plant of valuable nutrients.

Insectivorous Plants
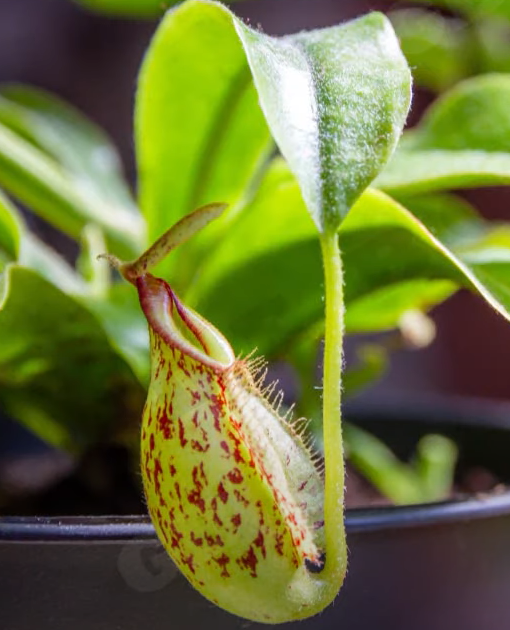
Plants that feed on insects are called insectivorous plants. The structure of these insectivorous plants which trap insects are actually modified leaves. Insectivorous plants are generally found in areas where soil lacks nutrients. They obtain additional nutrient supplements from the insects they trap. Insectivorous plants have special trapping mechanisms to catch their prey and they have special enzymes to absorb them. Pitcher Plant, Bladderworts, Sundew Plants and Venus Flytrap are examples of insectivorous plants.
Let`s know in detail how the Pitcher Plant traps insects:
- The pitcher-like or jug-like structure is the modified part of the leaf. The apex of the leaf forms a lid which can open and close the mouth of the pitcher. Inside the pitcher, there are hair which are directed downwards.
- When an insect lands in the pitcher, the lid closes and the trapped insect gets entangled into the hair.
- The insect is digested by the digestive juices secreted in the pitcher and its nutrients are absorbed.

Saprophytic Plants
Plants that obtain their nutrition from dead and decaying matter are called Saprophytic Plants. These plants dissolve the dead and decaying matter by secreting digestive juices and absorbing the nutrients. Mushrooms, yeasts and many bacteria are examples of Saprophytic Plants.
Symbiotic Plants
When two different types of plants live together by sharing both shelter and nutrients and mutually helping each other. Their association is called a symbiotic relationship. In organisms called lichens, a chlorophyll-containing partner, which is an alga, and a fungus live together. The fungus provides shelter, water and minerals to the alga and, in return, the alga prepares and provides food to the fungus.
How Nutrients are replenished in the Soil
- Plants absorb minerals and nutrients mainly – Phosphorous, Nitrogen and Potassium from the soil. So, their amounts in the soil keep on declining.
- To replenish the minerals & nutrients, farmers generally spread manure or fertilizers which are rich in phosphorous, nitrogen and potassium.
- Farmers add manure or fertilizers in their fields from time to time to maintain the fertility of the soil.
- Leguminous plants like peas, moong, beans etc. do not require nitrogenous fertilizers because a bacteria called Rhizobium can take atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into usable form. Plants use this usable nitrogen for their growth.
Solution of the Exercise
Why do organisms take food?
Solution:
All organisms require food to survive. Food gives them energy to perform various activities like
- to enable living organisms to build their bodies.
- to help them to grow
- to repair damaged parts of their bodies.
- to provide energy to carry out life processes.
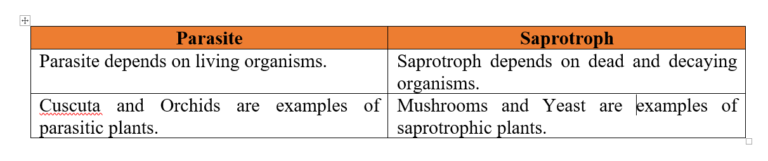
Distinguish between a parasite and a saprotroph.
How would you test the presence of starch in leaves?
Solution:
The presence of starch in leaves can be tested by Iodine Test:
- Remove chlorophyll from leaf by boiling it in alcohal.
- Put 02 drops of iodine solution on the leaf.
- The colour of the leaf will change to blue. This indicates the presence of starch in the leaf.
Give a brief description of the process of synthesis of food in green plants.
Solution:
Food is formed by the process of photosynthesis in green plants. The stages of photosynthesis are:
- The green pigment present in leaves, called Chlorophyll, traps sunlight. Plants use this energy during the photosynthesis process.
- Stomata present on the leaves take in Carbon dioxide from the air.
- Plants absorb water and minerals from the soil through their roots and transport it to the leaves.
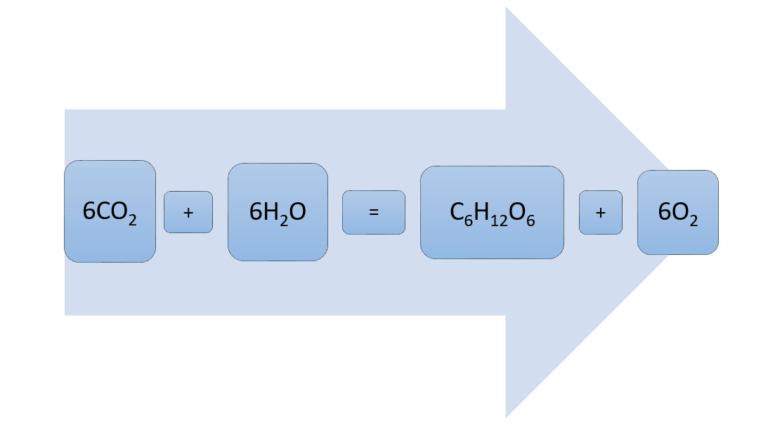
- Inside the chloroplast, the trapped sunlight energy is used to perform chemical reactions. The chemical reactions convert water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen.
- The chemical equation of photosynthesis is:
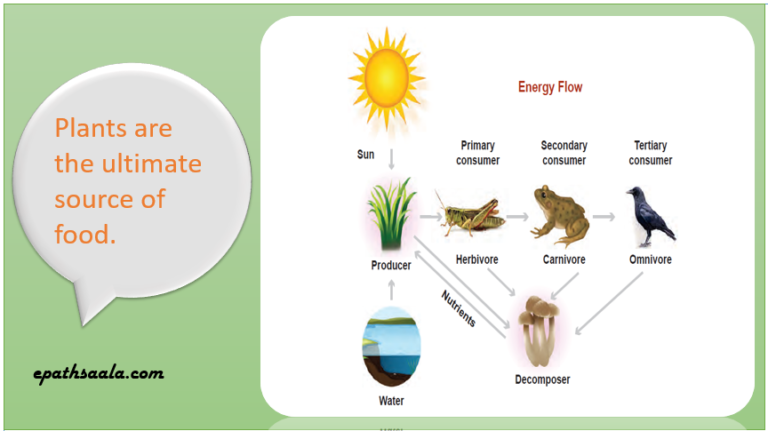
Show with the help of a sketch that plants are the ultimate source of food
Fill in the blanks
- Green plants are called _________________ since they synthesise their own food.
- The food synthesised by plants is stored as _________________.
- In photosynthesis solar energy is absorbed by the pigment called ___________.
- During photosynthesis plants take in ______________________ and release __________________ gas.
Solution:-
- autotrophs
- Starch
- Chlorophyll
- Carbon dioxide and Oxygen
Name the following
- A parasitic plant with yellow, slender and branched stem.
- A plant that is partially autotrophic.
- The pores through which leaves exchange gases.
Solution:
- Cascuta (Amarbel)
- Pitcher Plant
- Stomata
Tick the correct answer
- Cuscuta is an example of:
(i) autotroph (ii) parasite (iii) saprotroph (iv) host
- The plant which traps and feeds on insects is:
(i) Cuscuta (ii) china rose (iv) pitcher plant (iv) rose
Solution:
- Parasite
- Pitcher Plant
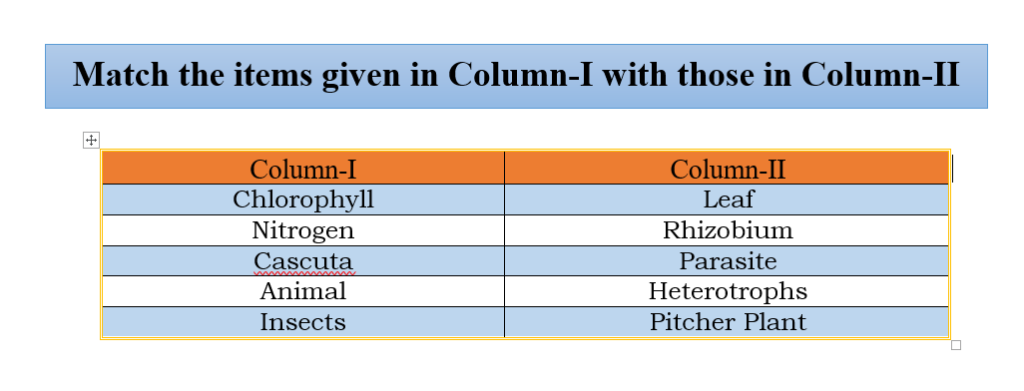
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II
Solution:
Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
- Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. (T/F)
- Plants which synthesise their food are called saprotrophs. (T/F)
- The product of photosynthesis is not a protein. (T/F)
- Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis. (T/F)
Solution:
- False (F). During photosynthesis, Oxygen is released.
- False (F). Plants which synthesize their food themselves are called autotrophs.
- True (T). The product of photosynthesis is oxygen and Carbohydrates.
- True (T). During photosynthesis plants trap solar energy and convert it into chemical energy.
Choose the correct option from the following:
Which part of the plant takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis?
(i) Root hair (ii) Stomata (iii) Leaf veins (iv) Petals
Solution: (ii) Stomata
Choose the correct option from the following:
Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their:
(i) roots (ii) stem (iii) flowers (iv) leaves
Solution: (iv) leaves
Why do farmers grow many fruits and vegetable crops inside large green houses? What are the advantages to the farmers?
Greenhouse provides favourable conditions like suitable heat, light etc. for the cultivation of many fruits and vegetables. Farmers get advantages like:
- It protects crops from diseases and adverse climatic conditions.
- It protects crops from wind and rodents.
- Farmers have bountiful crops.
- Farmer’s crops are also protected from birds and animals.
Objective Type Questions
Powered By EmbedPress