NCERT solutions: Class 6: Science-Sorting of materials into groups
NCERT notes alongwith solutions for class 6: science – Chapter “Sorting of materials into groups” are provided here. The notes as well as solutions are very much helpful for the students to understand the topics. The solutions will be handy for quickly completing the homework and preparing for exams.
Table of Contents
ToggleObject Around Us
- We see a wide variety of objects around us like a chair, a bullock cart, a cycle, cooking utensils, books, clothes, toys, water etc.
- All these objects have different shapes, sizes, colours and uses.
- These objects are either made from a single material or by combining different materials.
Let’s see the examples of:
- Objects and the materials they are made of
- Different types of objects that are made from the same materials
List of objects and the materials from which they are made of:
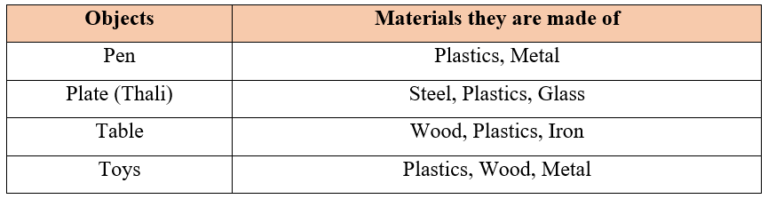
List of different types of objects that are made from the same materials
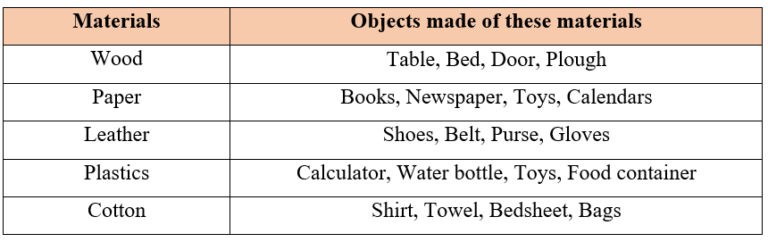
Sorting of materials into groups
Materials

Why there is a need to "Sorting of materials into groups"
Due to the vastness of objects, we need to group/ classify the objects for:
- placing similar types of materials in one place which assists us in locating the items easily.
- knowing the properties of any items easily because if we know the properties of any one member of the group, we can get an idea of the properties of other members of this group.
Basis of sorting of materials into groups
- Materials can be classified/ grouped based on the similarities and differences in their properties.
- We generally choose a material to make an object depending on its properties, and the purpose for which the object is to be used. So, let’s see here what are all the properties of materials.
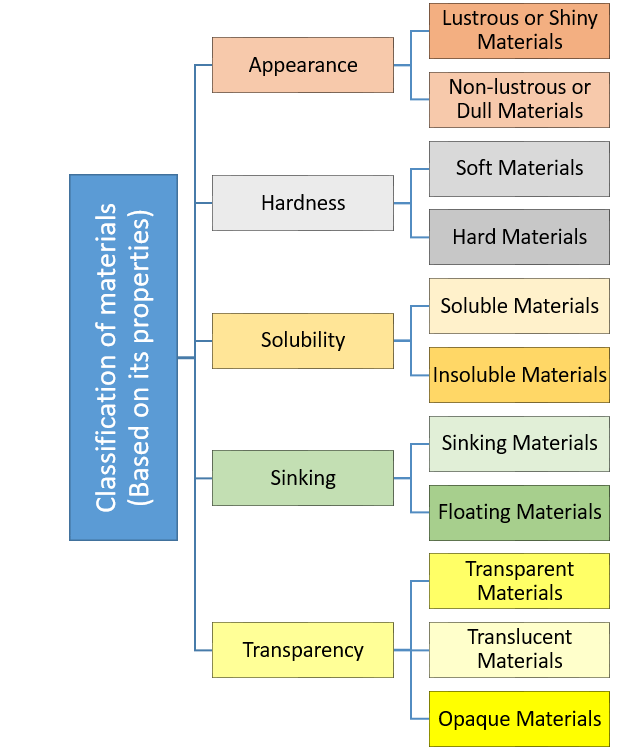
Sorting of materials into groups based on the following properties of materials:
- Appearance
- Hardness
- Soluble or Insoluble
- Float or Sink
- Transparency
Appearance
-
- Materials usually look different from each other. Wood looks very different from iron. Iron appears different from copper or aluminium.
- Based on appearance, there are two types of materials:
- Lustrous or shiny
- Non-lustrous or dull
Hardness
-
- Based on hardness, there are two types of materials:
- Soft materials
- Hard materials
- Based on hardness, there are two types of materials:
Soluble or Insoluble
-
- On the basis of solubility in water, materials can be classified as
- Soluble in water
- Insoluble in water
- On the basis of solubility in water, materials can be classified as
Soluble Materials: Materials that dissolve and therefore disappear in water are called soluble materials. For example: Sugar and Salt easily dissolve and disappear in water.
Insoluble Materials: Materials that do not dissolve and therefore do not disappear in water even after we stir them for a long time are called insoluble materials. For example – Sand, Sawdust, iron filings etc.
(Take a look in the next video. How sands will not dissolve and disappear in the water?)
Floating or Sinking in Water
-
- Materials that do not mix with water either float or sink in water. On this basis, materials can be classified as either floating or sinking materials.
- Floating materials
- Sinking materials
- Materials that do not mix with water either float or sink in water. On this basis, materials can be classified as either floating or sinking materials.
Floating Materials: Materials which do not mix with water and therefore float on the surface of water are called floating materials. For example: Oil, wood, ships, leaves, feathers etc.
(Take a look in the next video. How oil will not dissolve and float on the surface of the water?)
Sinking Materials: Materials which do not mix and settle down at the bottom of the water are called sinking materials. For example: sand, stone, steel spoon etc.
(Take a look in the next video. How sand will sink and settle down at the bottom of water?)
Transparency
- Different materials allow different amounts of light to pass through them. Based on this property of materials, materials are classified into three types:
- Transparent materials
- Translucent materials
- Opaque materials
- Transparent materials: – Transparent materials refer to those materials through which one can clearly see the objects. The reason behind this is that transparent materials allow almost all light to pass through them. For example – water, glass, air, some plastics etc.
- Translucent materials: – materials through which one can see things but not very clearly are called translucent materials. The reason is that translucent materials allow only a partial amount of light to pass through them. Translucent materials are also called semi-transparent materials. For example: oily patches on paper, tissue paper, muddy water, fog etc.
- Opaque materials: – Opaque materials refer to such materials through which one cannot see anything because opaque materials do not allow any amount of light to pass through them. For example: wood, steel, brick etc.
Summary of the sorting of materials into groups through relationship chart
Solution of the Exercise "Sorting of materials into groups"
1. List five objects which can be made from wood.
Ans: Five objects that can be made from wood are:
- Table
- Chair
- Wardrobe
- Doors
- Pencil
2. Select those objects from the following which shine:
Glass bowl, plastic toy, steel spoon, cotton shirt
Ans: Glass bowl and Steel spoon are the objects that shine.
3. Match the objects given below with the materials from which they could be made.
Remember, an object could be made from more than one material and a given material could be used for making many objects.
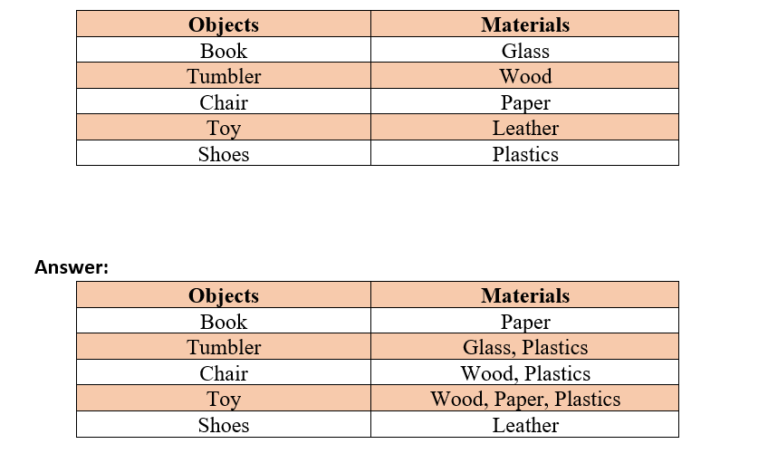
4. State whether the statements given below are True or False.
- Stone is transparent, while glass is opaque.
- A notebook has lustre while eraser does not.
- Chalk dissolves in water.
- A piece of wood floats on water.
- Sugar does not dissolve in water.
- Oil mixes with water.
- Sand settles down in water.
- Vinegar dissolves in water.
Explanation: A stone is indeed an opaque object. It does not allow any amount of light to pass through it. A glass is transparent. It allows almost all amounts of light to pass through it.
Explanation: lustrous is a property of metals due to which their surface shines or glows. A notebook is made from paper which is obtained from wood pulp which is a non-metal. So the surface of the notebook does not shine or glow. Whereas an Eraser is made from either natural or synthetic rubber which is a non-metal. So, the surface of the eraser does not shine or glow.
Explanation: Chalk is mainly made up of limestone (Calcium Carbonate). Calcium Carbonate has the characteristics of very low solubility in water. So, an extremely low amount of chalk can dissolve in the normal amount of water. Hence, chalk is said to be insoluble in water.
Explanation: Density and buoyancy made a piece of wood float on the surface of the water. The density of wood is lesser than that of the water. The buoyant force acts on the wood in an upward direction which is greater than that of gravity acting in the downward direction which keeps a piece of wood floating on water.
Explanation: Sugar or sucrose like water has bonds between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. And, similarly to water, the area near the oxygen is slightly negative, while the area near the hydrogen is slightly positive. The polar water molecules attract the negative and positive regions of the polar sucrose molecules, causing sucrose to dissolve in water.
Explanation: water molecules are polar molecules which means it has a positive charge at one end and a negative charge at the other end. Due to this, water molecules stick together because the positive end of one water molecule is attracted to the negative end of another. Whereas oil molecules are non-polar molecules. Its charge is evenly balanced. This means oil molecules are more attracted towards other oil molecules than water molecules, so the two never mix.
Explanation: Sand does not mix with water and the density of the sand is heavier than water. That`s why sand sinks and settles down at the bottom of the water.
Given below are the names of some objects and materials:
Water, basketball, orange, sugar, globe, apple and earthen pitcher Group them as:(a) Round shaped and other shapes (b) Eatables and non-eatables
Answer:
(a) Round shaped: Basketball, Orange, Globe, Apple and Earthen pitcher
(b) Other shapes: water and sugar
(c) Eatables: Water, Orange, Sugar, Apple
(d) Non-eatables: Basketball, Globe, Earthen pitcher
6. List all items known to you that float on water. Check and see if they will float on an oil or kerosene.
- Paper
- Wood
- Wax
- Ice
- Thermocol
- Paper
- Wax
- Thermocol
- Paper
- Thermocol
7. Find the odd one out from the following:
a) Chair, Bed, Table, Baby, Cupboard
b) Rose, Jasmine, Boat, Marigold, Lotus
c) Aluminium, Iron, Copper, Silver, Sand
d) Sugar, Salt, Sand, Copper sulphate
a) Baby – Others are made up of wood.
b) Boat – Others are flowers
c) Sand – Others are metals
d) Sand – Others are soluble in water.