NCERT Solutions: Class 6: Science: Getting to Know Plants
NCERT notes alongwith solutions for class 6: science – Chapter “Getting to Know Plants” are provided here. The notes as well as solutions are very much helpful for the students to understand the topic. The solutions will be handy for quickly completing the homework and preparing for exams.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction: Getting to Know Plants
We do see a variety of plants around us.
Some plants are small. some are big. Some have green leaves while others have different colours. Some have tender stems while some have hard stem.
Classification of Plants
- Based on the height, type of stem and where the branches appead:
- Herbs
- Shrubs
- Trees
- Two more classifications of plants which are different from the herbs, shrubs and trees are:
- Creepers
- Climbers
- Based on Flowering, plants are categorized into two types:
- Flowering
- Non-flowering
Classification of plants based on the height, type of stem and where the branches appead:
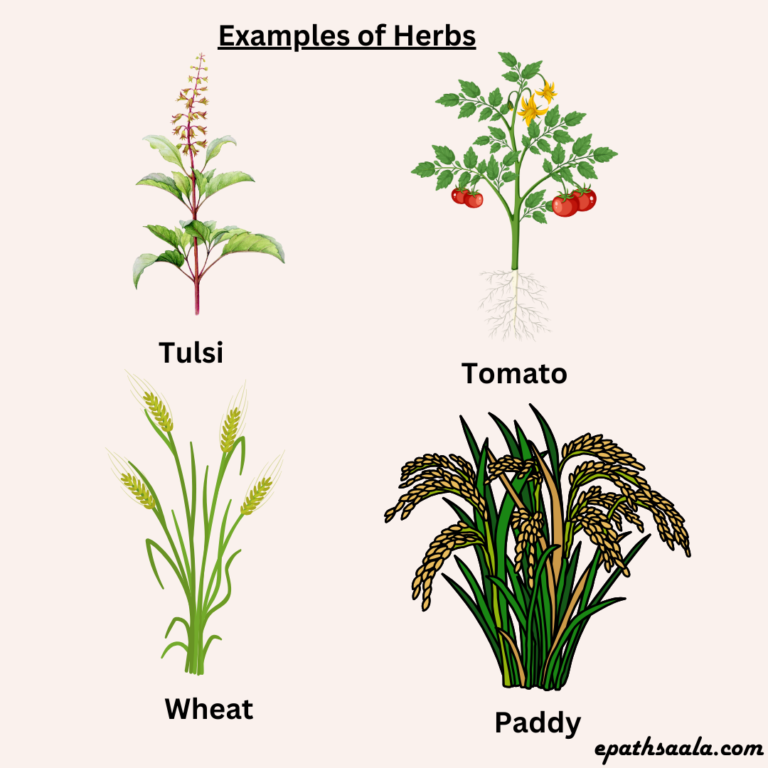
Herbs
Plants with green and tender stems are called herbs. They are usually short and may not have many branches. Tulsi, Tomato, Wheat, Paddy are the examples of herbs.
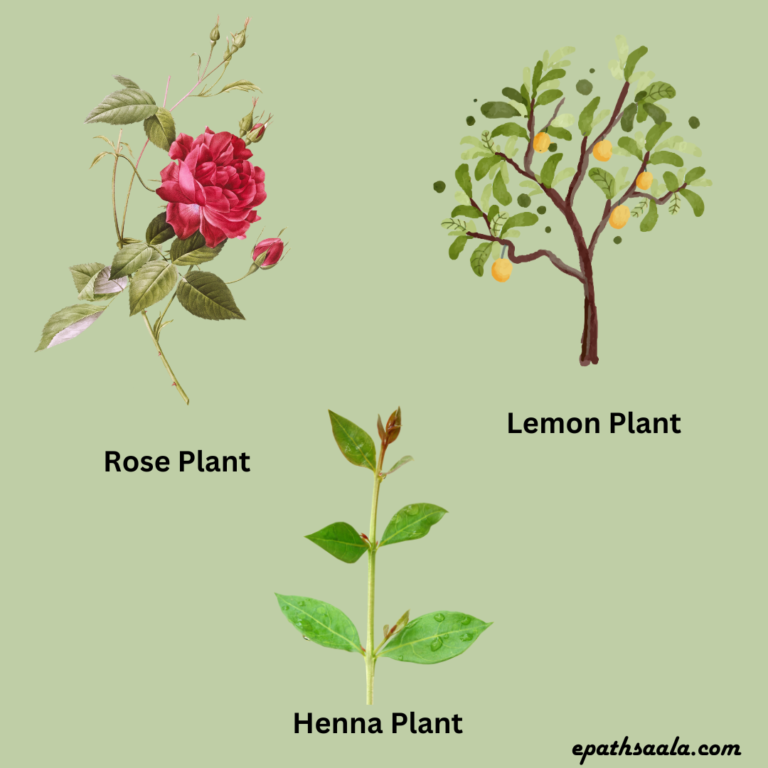
Shrubs
Shrubs have hard stems but not very thick. The branches of shrubs develop near the base of the stem. Rose, Lemon, Henna etc. are the examples of shrubs.
Trees
Trees are tall and have hard & thick stems. The stems have branches in the upper part much above the ground. For example – Mango tree, Neem tree, Oak tree etc.

Classification of plants which are different from the herbs, shrubs and trees:
Creepers
Plants with weak stems that cannot stand upright but spread on the ground are called creepers. For example – watermelon, pumpkin etc.

Climbers
Plants with weak stems that cannot stand upright but readily climb after receiving support are called climbers. Grapevine, Money plant, Jasmine etc.

Classification of plants based on flowering:
- Flowering Plants
- Non-flowering Plants
Flowering Plants
- Plants which bear flowers and seeds are called flowering plants.
- Flowering plants are also called angiosperms.
- Flowers are considered as the reproductive organs of plants because flowers are the place where sexual reproduction takes place.
- For example – Jasmine, rose, sunflower etc.
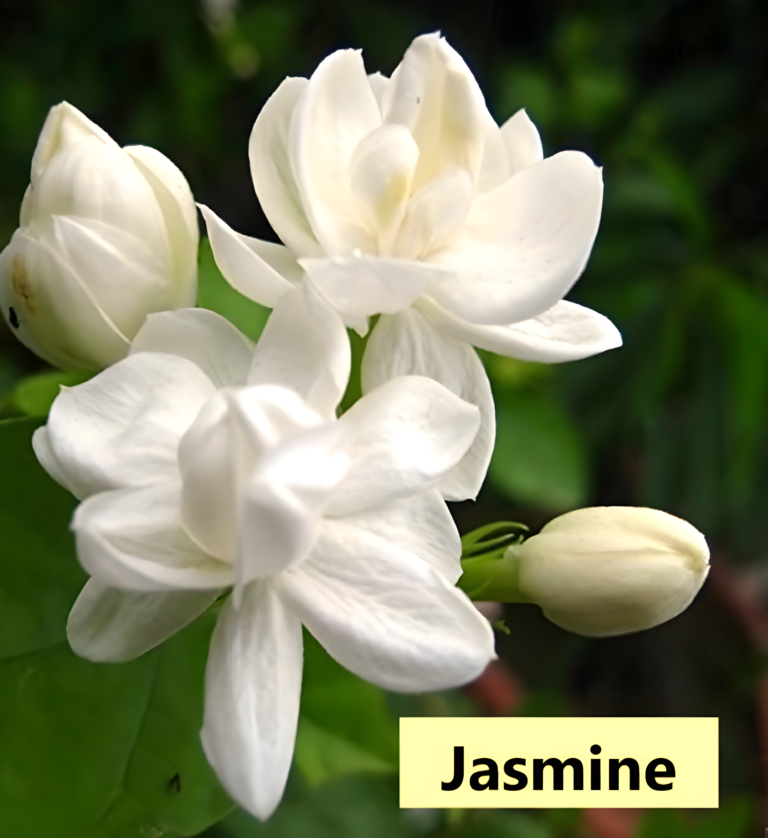



Non-flowering Plants
- Plants that do not produce flowers for reproduction are called non-flowering plants.
- Non-flowering plants are also called as gymnosperms.
- Ferns, Cycas, mosses etc. are examples of non-flowering plants because these plants do not bear flowers and fruits which are generally found in flowering plants.
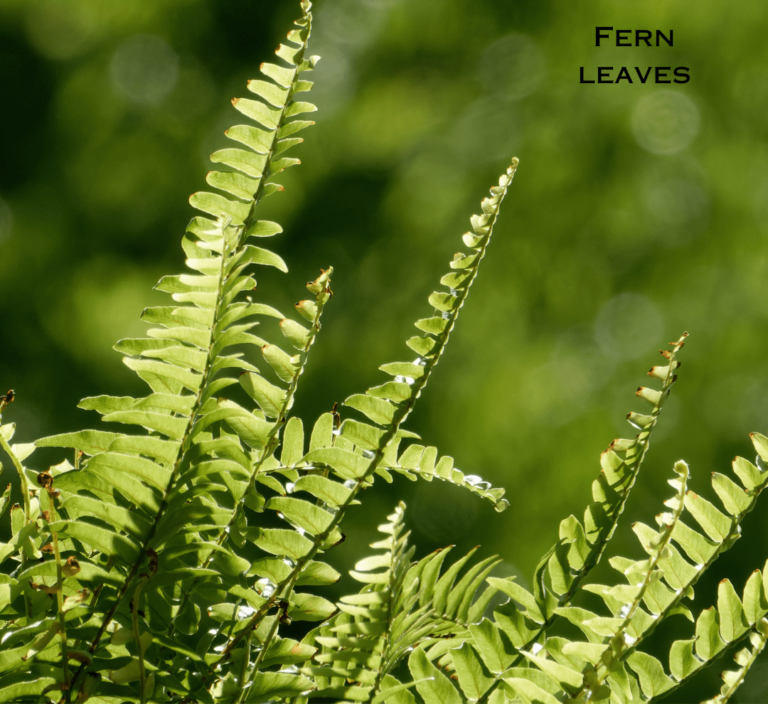
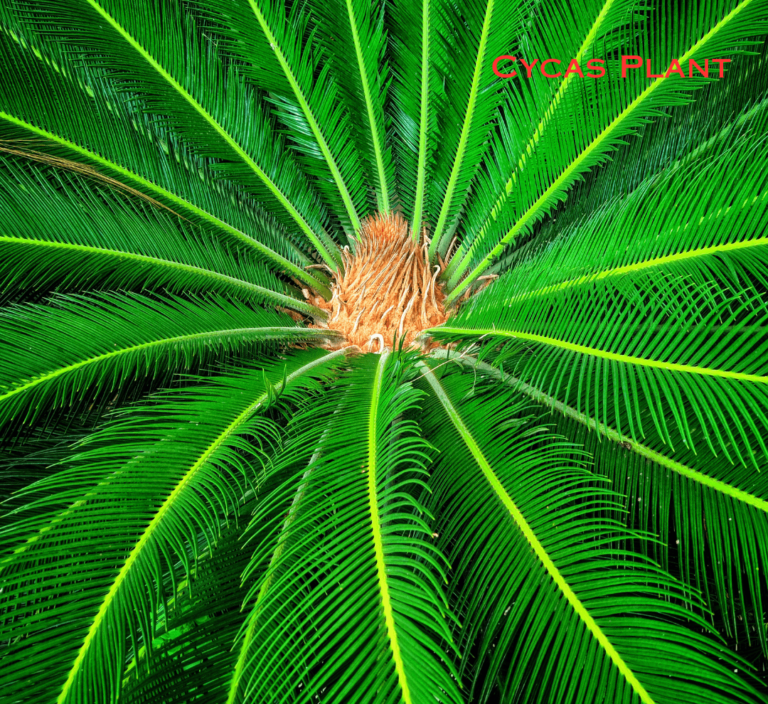



Parts of Plants
- A plant has two main parts.
- One part stays above the ground. This part of the plant is called the shoot system.
- The other part of the plant stays below the ground. This part of the plant is called the root system.
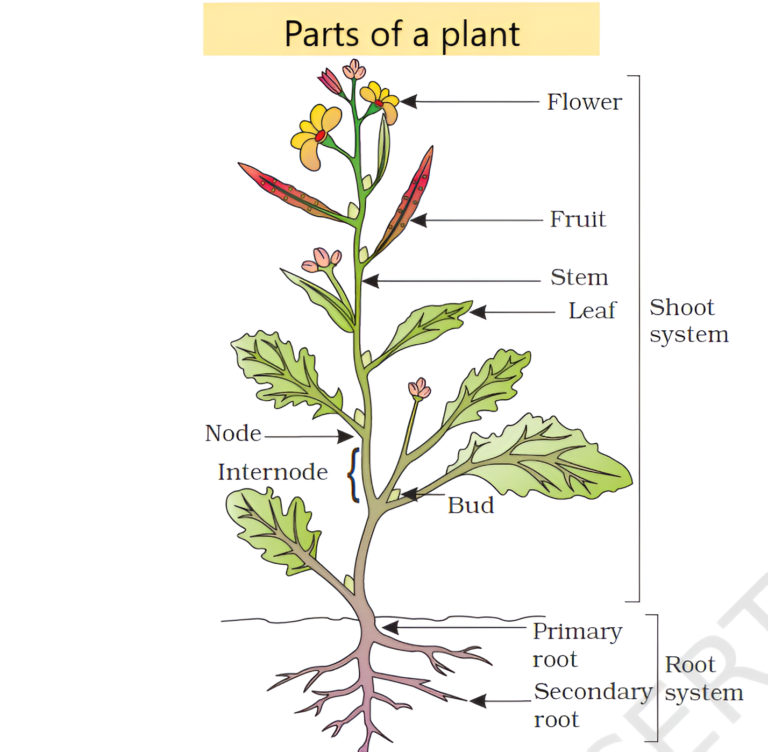
Shoot system
- This part of the plant stays above the ground.
- It includes:
- stems
- leaves
- buds
- flowers
- fruits
Stems
- Stems bear leaves, branches, buds, flowers and fruits.
- Stems provide support for standing in upright position.
- Stems can be soft & flexible or hard & rigid.
- The region of the stem where leaves are born is called node while internodes are the portions between two nodes.
- It helps in the upward movement of water.
- It transmits water and minerals to leaves and other parts attached to the stem.
- Some stems perform the function of storage of food, protection and of vegetative propagation.

Leaves
-
- A leaf is generally a green flattened structure borne on the stem.
- It is of two types:
- simple leaves
- compound leaves
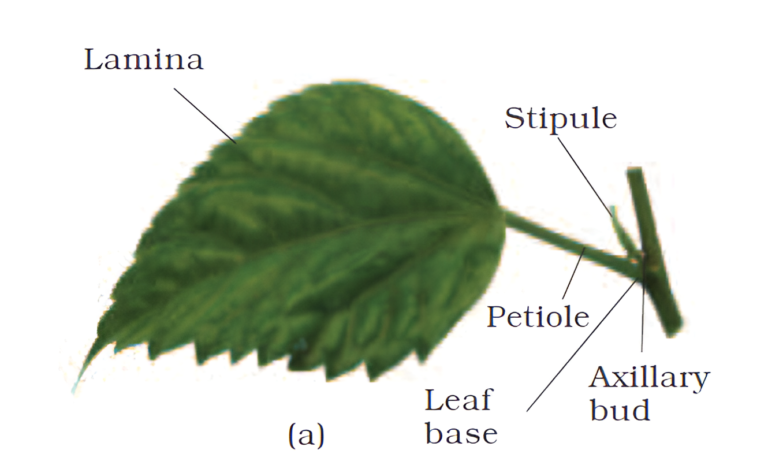
- A typical leaf consists of three main parts:
- leaf base
- petiole
- lamina
- Leaf base: This is the part where a leaf is attached to the stem.
- Petiole: A petiole is a slender stalk that joins the leaf blade to the stem of a plant.
- Lamina: The lamina is also known as the leaf blade. It is the green expanded part of the
leaf with veins and veinlets.
Functions of a leaf
There are two main functions of a leaf:
- Photosynthesis: A leaf carries a green pigment called chlorophyll and the leaf in the presence of sunlight, water, carbon dioxide and chlorophyll makes its own food. This process of manufacturing food by the leaves is called photosynthesis. Oxygen is released in this process.
2. Transpiration: It refers to the process through which leaves lose water in the form of water vapour. It helps in the absorption and upward movement of water and minerals from roots to leaves. It also helps the plant from heating up.
Other important terms related to leaves
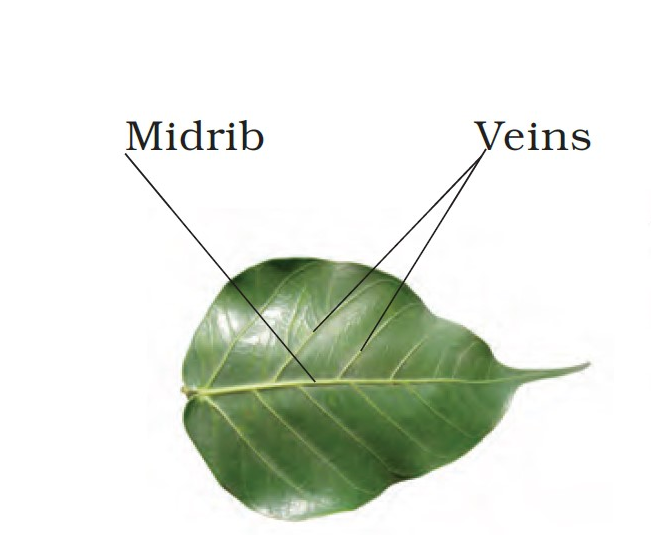
- Veins: The lines on the leaves are called veins.
- Midrib: A prominent line in the middle of the leaf is called a midrib.
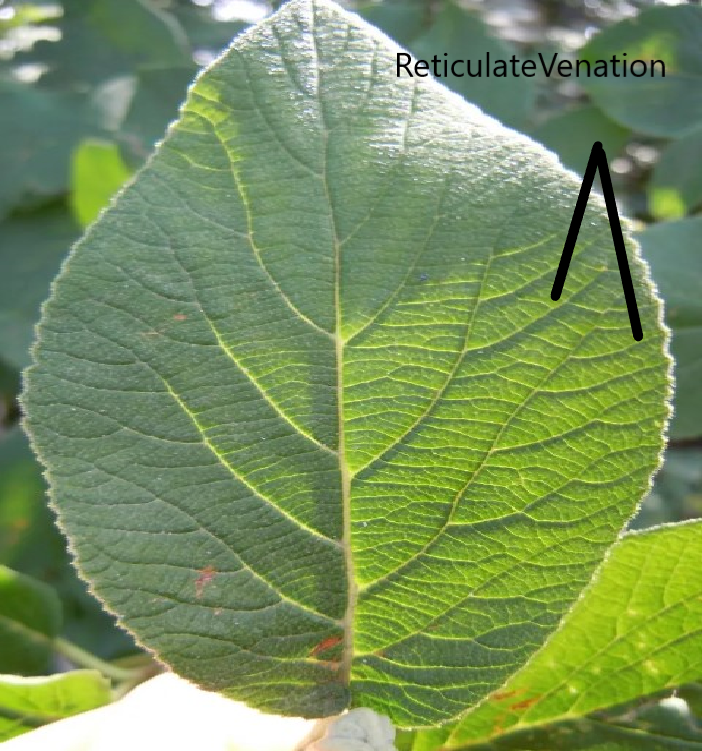
- Venation: The arrangement of veins and the veinlets in the lamina of a leaf is called venation.
- Leaf Venation: The designs made by veins in a leaf are called venation.
- Reticulate: If the design made by veins in a leaf is net-like on both sides of the midrib is called reticulate.
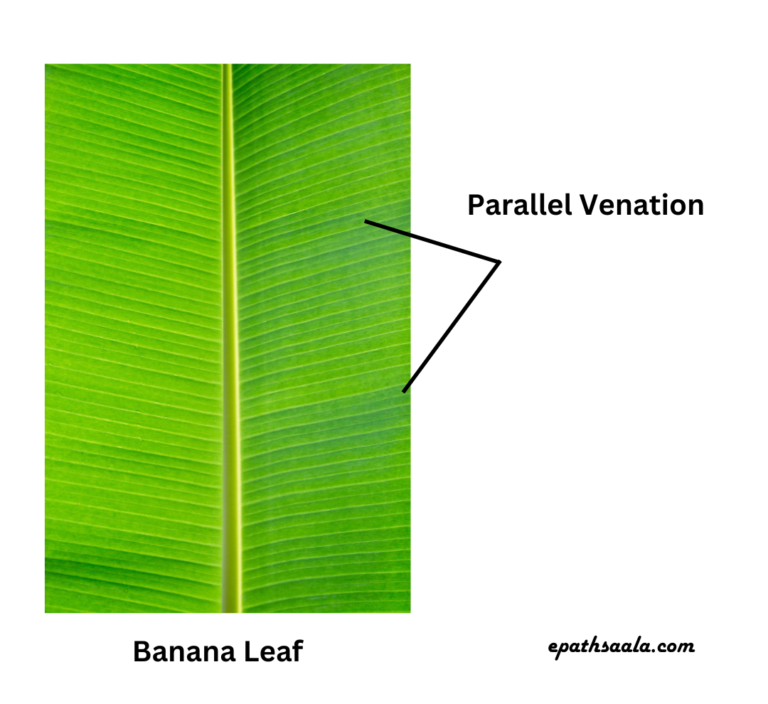
- Parallel Venation: when the veins run parallel to each other within a lamina, the venation is called parallel venation.

Buds
- Buds are underdeveloped or embryonic shoots that contain meristem tissue.
- It can give rise to new leaves, flowers or stems.
- There are two types of buds: terminal buds and lateral buds.
- The terminal buds are generally found at the tips of branches whereas the lateral buds are found along the sides of a plant.
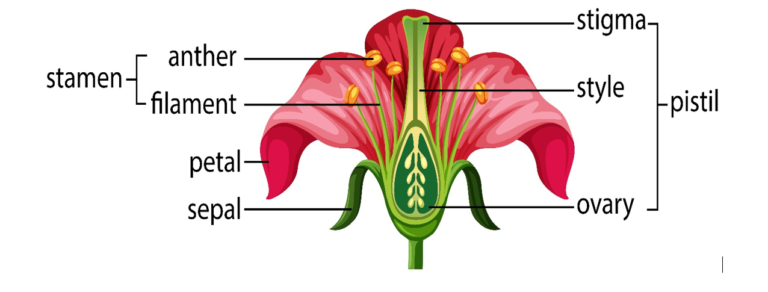
Flowers
- A flower is the reproductive unit of a plant. It is meant for sexual reproduction.
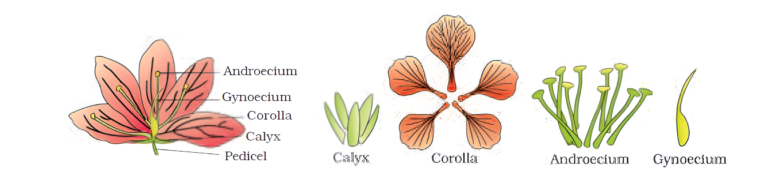
- There are four main parts of a typical flower:
-
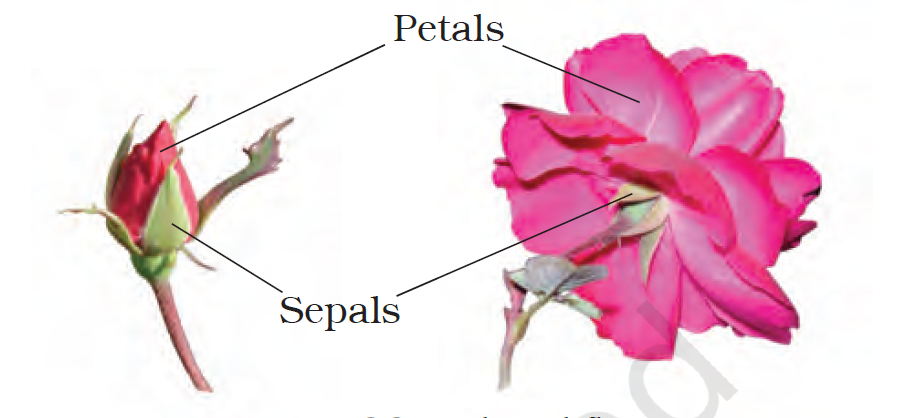
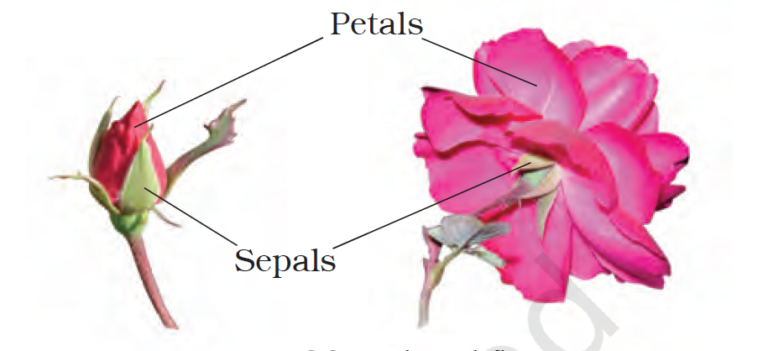
- Calyx (Sepals)
- Corolla
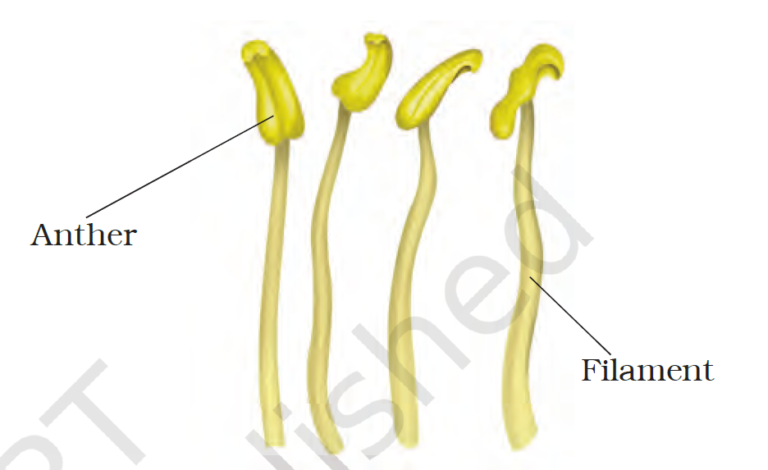
- Androecium
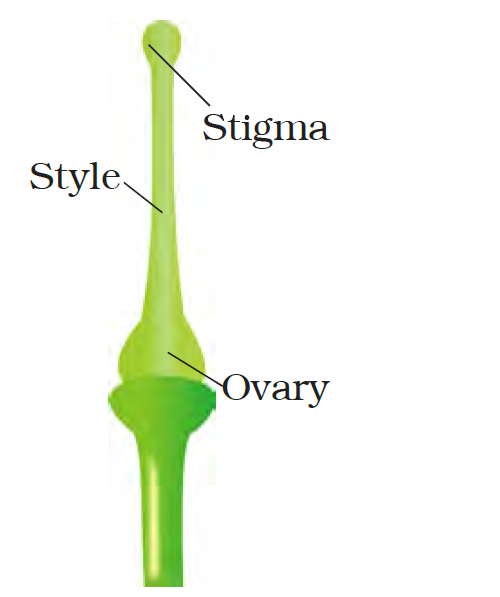
- Gynoecium (Carpel)
- Calyx(Sepals) – It is the outermost whorl of the flower and the members are called sepals. Generally, sepals are green, leaf like and protect the flower in the bud stage.
- Corolla – Corolla is composed of petals. Petals are usually brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination. The shape and colour of corolla vary greatly in plants.
- Androecium – Androecium is composed of stamens. Each stamen which represents the male reproductive organs consist of a stalk or a filament and an anther.
- Gynoecium – Gynoecium is the female reproductive part of the flower and is made up of one or more carpels. A carpel, also called pistil, consist of three parts namely – stigma, style and ovary. Stigma is actually at the tip of the style and is the receptive surface for pollen grains. The style connects the ovary to the stigma. Ovary is the enlarged basal part on which lies the elongated tube, the style.
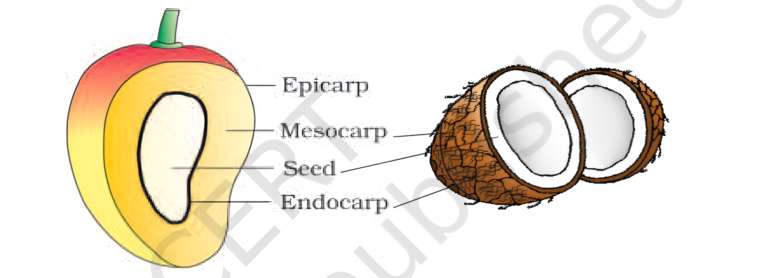
Fruits
- A fruit is a characteristic feature of the flowering plants.
- It is a mature or ripened ovary, developed after fertilisation.
- Generally, the fruit consists of a wall or pericarp and seeds. The pericarp is differentiated into the outer epicarp, the middle mesocarp and the inner endocarp.
Root System
- The root system stays below the ground. A root is a part of the plant that grows below the ground and helps anchor the plant firmly in the soil. It absorbs water and minerals from the soil and transmits it to the stem through the xylem of the plant.
- Based on the difference in structure of the roots, the roots are categorized into three types:
- tap root system
- fibrous root system
- adventitious root system
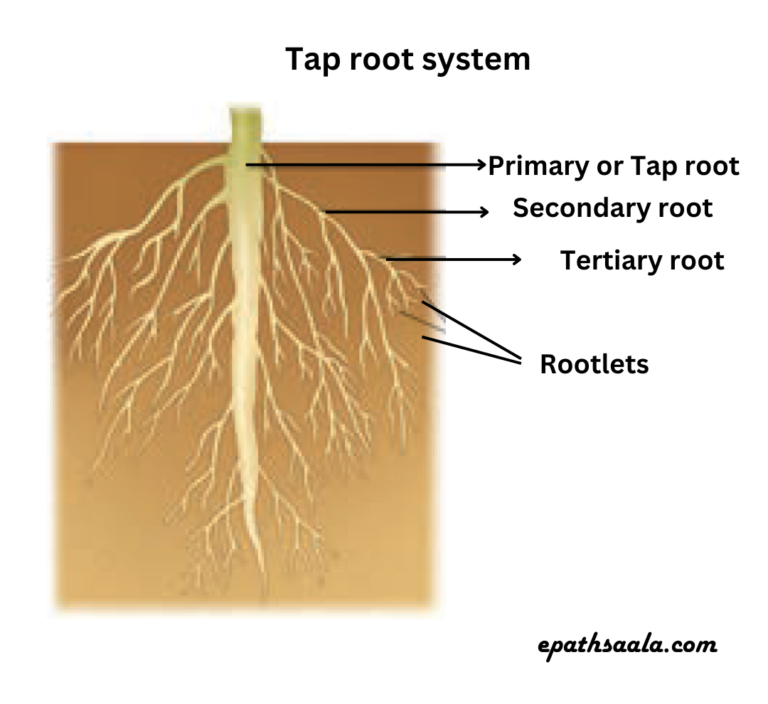
- Tap root system: The primary and its branches (secondary & tertiary roots) constitute the tap root system. A primary root is the direct elongation from the embryonic radicle which grows inside the soil. For example – Mustard Plant.
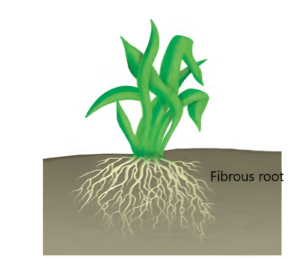
- Fibrous root system: In monocotyledons plants, the primary root is short lived and is replaced by a large number of roots. These roots originate from the base of the stem and constitute the fibrous root system. For example – Wheat Plant.
- Adventitious root system: In some plants like grass and banyan tree, roots arise from parts of the plant other than the radicle and are called adventitious root.


Main functions of root
- absorption of water and minerals from the soil
- providing anchorage to the plant parts
- storing reserve food material and synthesis of plant growth regulators
Solution of the Exercise (Getting to know plants)
Correct the following statements and rewrite them in your notebook.
- Stem absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
- Leaves hold the plant upright.
- Roots conduct water to the leaves
- The number of petals and stamens in a flower is always equal.
- If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are also joined together.
- If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is joined to the petal.
Solution.
- Root absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
- Stems hold the plant upright.
- Stems conduct water to the leaves
- The number of petals and stamens in a flower may be equal or different in different flowers.
- If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals may or may not be joined together.
- If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is not necessarily joined to the
petal.
Draw (a) a leaf, (b) a taproot and (c) a flower, you have studied for Table 4.3
The pics of a leaf, a taproot and a flower are given below:

Can you find a plant in your house or in your neighborhood, which has a long but weak stem? Write its name. In which category will you place it?
Solution
Yes. Money plant has a long but weak stem. It will be placed under “Creeper” category.
What is the function of a stem?
Solution
The main functions of a stem are:
- It provides support to the branches, leaves, flowers and fruits.
- It transmits water and minerals to leaves and other parts attached to the stem.
- Some stems perform the function of storage of food, protection and of vegetative propagation.
Which of the following leaves have reticulate venation? Wheat, tulsi, maize, grass, coriander (dhania), China rose
- Tulsi, Corainder (Dhania) and China rose have reticulate venation.
- While the others – wheat, maize and grass have parallel venation.
If a plant has fibrous root, what type of venation do its leaves have?
Solution
- If a plant has fibrous roots, its leaves will have parallel venation like wheat, maize etc.
If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, what kind of roots will it have?
Solution
- If a plant has leaves with reticulated venation, then its root is likely to have tap roots. For example, a carrot or a rose plant has leaves with reticulate venation and its roots are called tap roots.
Is it possible for you to find out whether a plant has taproot or fibrous roots by looking at the impression of its leaf on a sheet of paper?
Solution
- Yes. It is possible to determine whether a plant has a tap root or a fibrous root by looking at the impression of its leaf on a sheet of paper.
- If the leaf of the plant has parallel venation, then its root will be a fibrous root. And if the leaf of the plant has reticulate venation then its root will be a tap root.
What are the parts of a flower?
Solution
- Broadly, there are four main parts of a flower as depicted in the picture given below:
From the following plants, which of them have flowers? Grass, maize, wheat, chilli, tomato, tulsi, peepal, shisham, banyan, mango, jamun, guava, pomegranate, papaya, banana, lemon, sugarcane, potato, groundnut
Solution
- The following plants have flowers:
- Maize, wheat, chili, tomato, tulsi, pipal, shisham, banana, mango, Jamun, guava, pomegranate, papaya, banana, lemon, and potato.
Name the part of plant which produces food. Name the process.
Solution
- Leaves are the part of the plant that makes food. The leaves through the photosynthesis process make food for the plant.
In which part of a flower, you will find the ovary?
Solution
- In flowers, an ovary is found in the pistil.
Name two plants in which one has joined sepals and the other has separate sepals.
Solution
- Plants with joined sepals are – Hibiscus (china rose).
- Plants with separated sepals are – Rose