Acids Bases and Salts: Class 7: Science: NCERT Solutions
NCERT notes alongwith solutions for class 7: science – Chapter “Acids Bases and Salts” are provided here. The notes as well as solutions are very much helpful for the students to understand the topics. The solutions will be handy for quickly completing the homework and preparing for exams.
Table of Contents
ToggleAcids Bases and Salts
Acids
- The word acid comes from the Latin word acere which means sour.
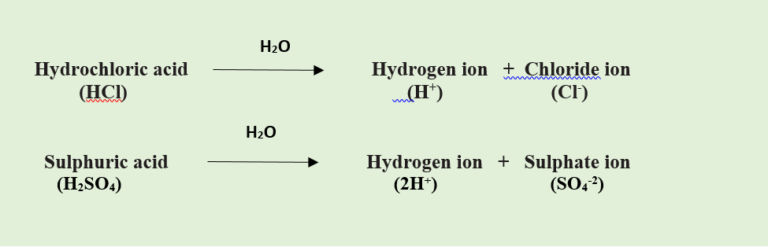
- Acids are chemical substances that release hydrogen (H+) ions when dissolved in water.
- For example, Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) and Nitric acid (HNO3) release hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water.
Types of acids
Acids can be classified into organic acids and inorganic acids depending on the sources.
Organic acids
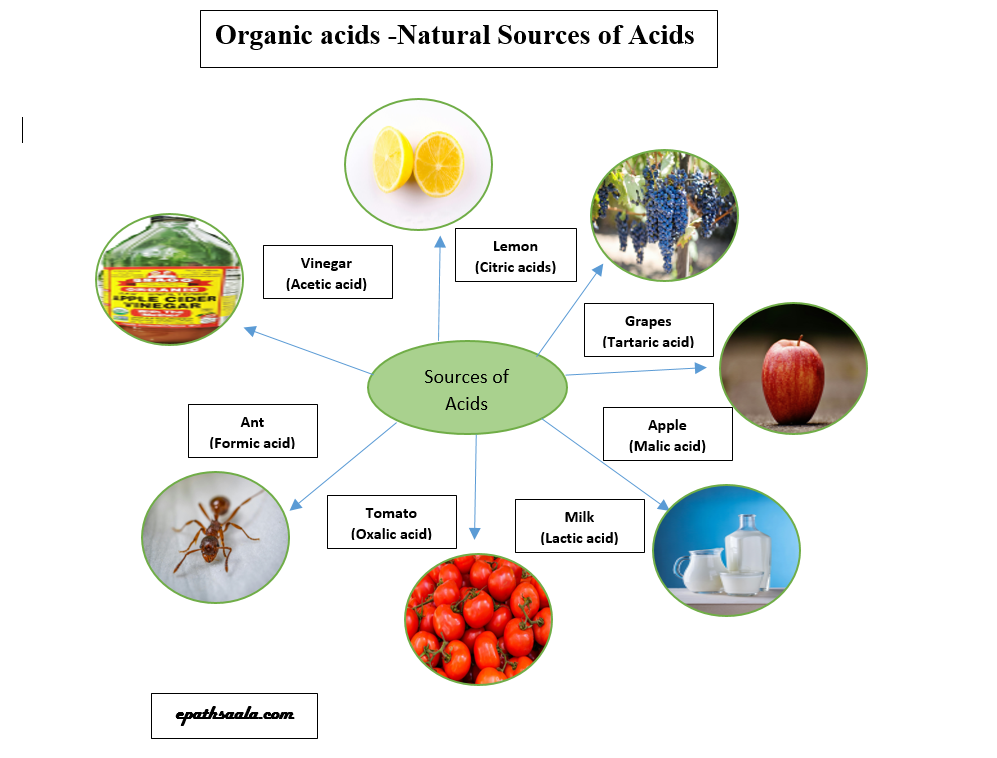
- Acids which occur naturally are called organic acids.
- These acids are generally found in fruits and vegetables. Some examples of organic acids and their sources are:
Inorganic acids
- Acids which are produced artificially are called inorganic acids or mineral acids.
- Examples: Hydrochloric acid (HCl),Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), Nitric acid (HNO3) etc.
Physical properties of acids
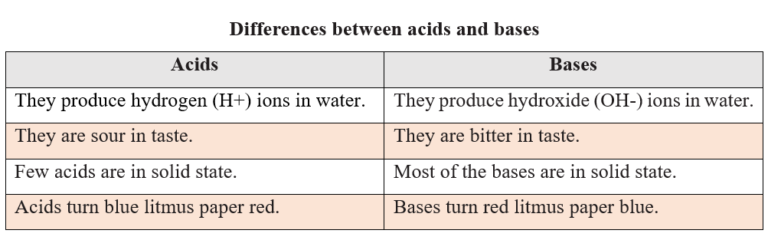
- Acids are sour in taste.
- They are corrosive in nature. Strong acids can spoil substances like human skin, clothes and paper.
- Acids are colourless.
- Acids change the colour of the indicators. Blue litmus paper turns red and methyl orange turns pink when treated with acids.
- They are soluble in water.
- Solutions of acids conduct electricity due to ionisation in water.
Uses of acids
- Hydrochloric acid present in our stomach helps in the digestion of food materials.
- Vinegar (acetic acid) and Benzoic acid are used to preserve food materials.
- Sulphuric acid (king of chemicals) is an effective dehydrating agent. It is used in various industries to make detergents, paints, fertilizers and many more chemicals.
- Hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and sulphuric acid are important laboratory reagents.
- Cells of all living organisms contain the fundamental nuclear material called nucleic acids. Animals have deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) whereas plants contain ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Bases
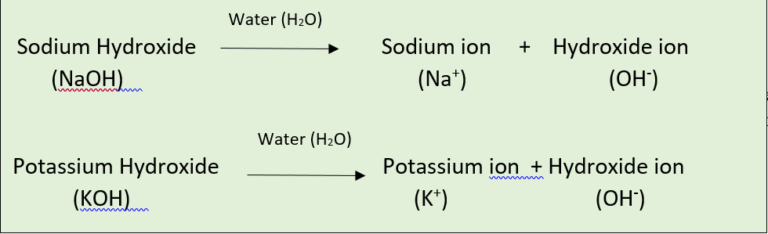
- The chemical substances that release hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are called as bases.
- Examples: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and Potassium hydroxide (KOH).
- However, there are certain chemical substances which do not release hydroxide ions when dissolved in water also behave as bases.
- Examples: Sodium carbonate, Sodium bicarbonate, Calcium carbonate etc.
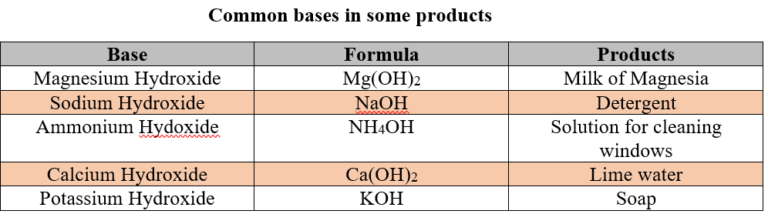
Bases we use in our daily life

Physical properties of bases
- Bases give soapy touch only in aqueous medium not in dry nature.
- Bases are bitter in taste.
- Bases are corrosive in nature. When come in contact with the skin frequently they form painful blisters.
- Bases are generally colourless.
- Bases also change the colour of the indicators. Red litmus paper turns blue when treated with bases. Similarly, they turn methyl orange to yellow and phenolphthalein to pink colour.
- Bases also conduct electricity in an aqueous solution.
Uses of bases
- Potassium hydroxide is used to make bathing soaps.
- Sodium hydroxide is used to make washing soaps.
- Sodium hydroxide is also used in paper industries, textile industries and in the preparation of medicines.
- Calcium hydroxide is used for white washing.
- Aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxides are used in antacids to cure acidity problems.
- Ammonium hydroxide is used to manufacture fertilizers, nylon, plastics and rubber.
Difference between acids and bases
Indicators
- Indicators are those substances which are used to test whether a substance is acidic or basic.
- The indicators change their colour when added to a solution containing an acidic or a basic substance.
- Litmus Turmeric, China rose petals (Gudhal) etc., are some of the naturally occurring indicators.
Types of Indicators
- There are two types of indicators. One is natural indicators and the other one is synthetic indicators.
Natural Indicators
- Natural indicators are chemical substances which are obtained from natural resources.
- Litmus, turmeric juice, China rose petals etc. are the indicators obtained from natural resources.
Litmus
- It is extracted from lichens.
- It has a mauve (purple) colour in distilled water.
- When added to an acidic solution, it turns red and when added to a basic solution, it turns blue.
- It is available in the form of a solution, or in the form of strips of paper, known as litmus paper.
Turmeric
- In acidic solution, turmeric indicator paper has no change in colour. That means it remains yellow.
- In the basic solution, the colour changes from yellow to red.
China rose petals
- In an acidic solution, the colour will be changed to deep pink or deep red.
- In the basic solution, the colour will be changed to green.
Synthetic Indicators
- An indicator prepared from artificial substances is known as synthetic indicators.
- Phenolphthalein and methyl orange are examples of synthetic indicators
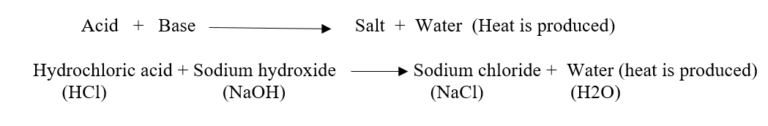
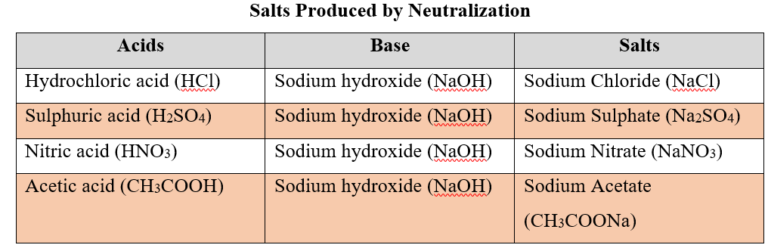
Neutralization
- The reaction between an acid and a base is known as neutralisation. Salt and water are produced in this process with the evolution of heat.
- When an acid solution and a base solution are mixed in suitable amounts, both the acidic nature of the acid and the basic nature of the base are destroyed.
- The resulting solution is neither acidic nor basic. Salt and water are produced with the evolution of heat.
- The solutions which do not change the colour of either red or blue litmus are known as neutral solutions.
Neutralisation in everyday life
- The solutions which do not change the colour of either red or blue litmus are known as neutral solutions.
Indigestion
- Our stomach contains hydrochloric acid. It helps us to digest food. But too much of acid in the stomach causes painful indigestion.
- To relieve indigestion, we take an antacid such as milk of magnesia, which contains magnesium hydroxide.
- It neutralises the effect of excessive acid.
Ant bite
- When an ant bites, it injects the acidic liquid (formic acid) into the skin.
- The effect of the acid can be neutralised by rubbing moist baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) or calamine solution, which contains zinc carbonate.
Soil treatment
- When the soil is too acidic, it is treated with bases like quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide).
- If the soil is basic, organic matter (compost) is added to it. Organic matter releases acids which neutralise the basic nature of the soil.
Solution of the Exercise
1. State differences between acids and bases.
Sol:
The differences between acids and bases are:

2. Ammonia is found in many household products, such as window cleaners. It turns red litmus blue. What is its nature?
Sol: As we know, red litmus paper turns blue when treated with bases. So, ammonia is a base.
3. Name the source from which litmus solution is obtained. What is the use of this solution?
Sol: Litmus solution is extracted from lichens. Litmus solution is used to determine whether a given item is acidic or basic. Acids turn blue litmus to red and basic turns red litmus to blue.
4. Is the distilled water acidic/basic/neutral? How would you verify it?
Sol: Distilled water is neutral which means that it is neither acidic nor basic. The same can be verified by using red and blue litmus strips. The colour of either red or blue litmus strips will not be changed in distilled water. This proves that distilled water is neutral.
5. Describe the process of neutralisation with the help of an example.
Sol: When an acid solution and a base solution are mixed in suitable amounts, both the acidic nature of the acid and the basic nature of the base are cancelled. The resulting solution is neither acidic nor basic. Salt and water are produced with the evolution of heat.

6. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
- Nitric acid turns red litmus blue. (T/F)
- Sodium hydroxide turns blue litmus red. (T/F)
- Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid neutralise each other and form salt and water. (T/F)
- Indicator is a substance which shows different colours in acidic and basic solutions. (T/F)
- Tooth decay is caused by the presence of a base. (T/F)
Sol:
- False (As we know, an acid turns blue litmus to red. Here, nitric acid is acidic in nature. So, the colour of red litmus will not change)
- False (As we know, sodium hydroxide is a base and it turns red litmus into blue.)
- True
- True
- False (Generally tooth decays due to the presence of bacteria in our mouth. The bacteria decompose food particles stuck in the gaps between our teeth thereby causing acid formation which leads to tooth decay.)
7. Dorji has a few bottles of soft drink in his restaurant. But, unfortunately, these are not labelled. He has to serve the drinks on the demand of customers. One customer wants acidic drink, another wants basic and third one wants neutral drink. How will Dorji decide which drink is to be served to whom?
Sol: Dorji can decide which drink is to be served to whom (customer) by doing the litmus paper tests in the following way:
- If the drink turns blue litmus paper to red, then the drink is acidic in nature and hence the drink will be served to such customer who wants an acidic drink.
- If the drink turns red litmus paper to blue, then the drink is basic in nature and hence the drink will be served to such customer who wants a basic drink.
- If the colour of the drink does not change with litmus paper, then it will be a neutral drink. Hence, this drink will be served to a third type of customer who wants a neutral drink.
8. Explain why:
- An antacid tablet is taken when you suffer from acidity.
- Calamine solution is applied on the skin when an ant bites.
- Factory waste is neutralised before disposing it into the water bodies.
Sol:
- An antacid tablet contains milk of magnesia which is a base. It reacts with acids and neutralises its effects. Thereby we feel relief.
- When an ant bites, it injects formic acid. Calamine solution contains zinc carbonate which is basic in nature. Thus, it neutralizes the acid effect of the ant bite when applied on the skin.
- The wastes of many factories contain acids. If they are allowed to flow into the water bodies, the acids will kill aquatic organisms. The factory wastes are, therefore, neutralized by adding basic substances.
9. Three liquids are given to you. One is hydrochloric acid, another is sodium hydroxide and third is a sugar solution. How will you identify them? You have only turmeric indicator.
Sol: Take a few drops of each solution in three separate test tubes. Now do the test in the following way:
- Put a turmeric indicator in each of the test tubes. The solution which changes the colour of the indicator to red is basic and the solution must be sodium hydroxide.
- Now put a few drops of sodium hydroxide in the other two test tubes to obtain two separate mixtures.
- One by one put a few drops of each mixture on the turmeric indicator. The mixture which changes the colour of the indicator to red contains a neutral sugar solution. Whereas the mixture which does not show any colour change in the indicator contains hydrochloric acid which was neutralized with the addition of sodium hydroxide.
10. Blue litmus paper is dipped in a solution. It remains blue. What is the nature of the solution? Explain.
Sol: If a blue litmus paper when dipped in a solution, remains blue, it implies that the solution is either basic or neutral.
11. Consider the following statements:
(a) Both acids and bases change colour of all indicators.
(b) If an indicator gives a colour change with an acid, it does not give a change with a base.
(c) If an indicator changes colour with a base, it does not change colour with an acid.
(d) Change of colour in an acid and a base depends on the type of the indicator.
Which of these statements are correct?
(i) All four (ii) a and d (iii) b, c and d (iv) only d
Sol: (iv) only d
(The change of colour in an acid and a base depends on the type of the indicator. For example, a blue litmus doesn’t exhibit any change with a basic solution but it turns to red in an acidic medium and the reverse takes place in the case of a red litmus. Hence, d is the only correct statement.)